MARCH 28, 2022
10 min read
Since January 2015, traditional banks around the United Kingdom have closed or scheduled the closure of 4,735 branches, at a rate of around 54 per month.
The cause is the fact that more and more customers are choosing to bank online rather than in person. That is why digital banking and especially neo banks are taking their place under the sun by implementing one or several proven business models. Different approaches towards these models and their combination will shape the future of fintech for the next several years. So, let’s find out what these models are, and how they are currently used.
Buy Now, Pay Later (BNPL)
The recent rise of BNPL products has already changed the way consumers spend their money. Like some overdrafts, BNPL also offers short-term interest-free loans, though only for purchases.
However, while overdrafts may be interest-free for up to one month, BNPL loans are typically interest-free for up to three months.
Interestingly, over the past couple of years, traditional financial institutions have been losing eight to ten billion dollars in revenue per year because customers chose fintech BNPL offers over banking loans.
A great example from the UK is Klarna, which partners with retailers all over the world, giving their customers tools to shop directly from corresponding sites. The customer pays 30 days later or splits the cost into 3 interest-free monthly installments.
Advantages of the BNPL model:
- Lower regulation. The BNPL model is relatively new and is not overregulated. The UK Treasury is only taking the first steps to explore policy options for regulating the BNPL industry.
- Easy marketing. BNPL tools hit the bull’s eye in meeting customers’ demand and therefore are advertised rather easily as an attractive and appealing feature.
- Ready tools. Financial institutions such as Mastercard and Visa are also competing to develop BNPL options that will allow them to keep transactions in their systems. Mastercard’s BNPL option is available to banks, fintech firms, etc. Visa offers BNPL as well, with a handy toolbox that enables card issuers to create installment plans.
Drawbacks of the BNPL model:
- Risks in case the customer cannot meet payment deadlines and their debt becomes a liability.
Subscription
Nowadays, virtually everyone pays monthly for such online services as Netflix, YouTube Premium, Spotify, or Amazon Prime. As these providers created straightforward services with multiple plans and options, consumers rushed for intellectual and virtual products. For the same reasons, neo banks are using a subscription model.
In the subscription model, customers pay recurring fees for access to a certain range of services, while a chosen plan determines a constant rate, which can be charged on autopay.
Subscription business model is easy to implement, as all you need to do may be simplified to these three steps:
- Develop a pricing and bundle strategy
- Give a way for customers to manage subscriptions
- Scale the infrastructure.

In banking, different subscription plans provide customers with a growing number of features and services. For example, Revolut offers four plans: Standard, Plus, Premium, and Metal, which differ in customer support priority, withdrawal fees, investment opportunities, flight bonuses, and card design. In 2020, Revolut increased its subscription revenue by 92% in a single year, making the subscription one-third of its income.
Advantages of the subscription model:
- Predictable revenues. Customers would rather stay with a service, than cancel the subscription, so service providers can predict their revenues easier and implement long-term planning.
- Stronger customer relationships. The longer the customer is subscribed to your product, the harder it is for them to cancel. Having paid for the subscription, customers will most likely choose between offers included in their plan and not among competitors’ proffers. Also, service providers hold a unique position to easily collect customer feedback.
- Simplicity. The subscription model makes products easy to advertise and to sell as it has a simple set-up process and no hidden fees, providing customer-attractive offers.
Drawbacks of the subscription model:
- High initial investments. Before introducing subscription plans, you should develop various services to be included in the plans, which would be time-and-money-consuming.
- Initial customers attraction. The first round of marketing is the most important as you need to engage your first customers.
- Providing constant value. Despite that customers tend to keep on the subscription, you as a business need to keep increasing your offers’ quality and continually update your products.
Interchange Fee
Each time we pay with our cards, either at point of service (POS terminal), online or with PayPass (card not present — CNP) a number of commissions are charged from merchants that is usually called interchange fee. This fee associates with card payment licensing.
There are two general types of card payment schemes: four-party and three-party.
In a four‑party scheme, the licenser sets the terms of the deal between the issuer and the acquirer. For example, MasterCard operates a card payment system in which it grants licenses to payment service providers (PSPs) to issue cards and acquire commission but does not undertake its own issuing or acquiring. The card payment licensors mostly use a four-party scheme.
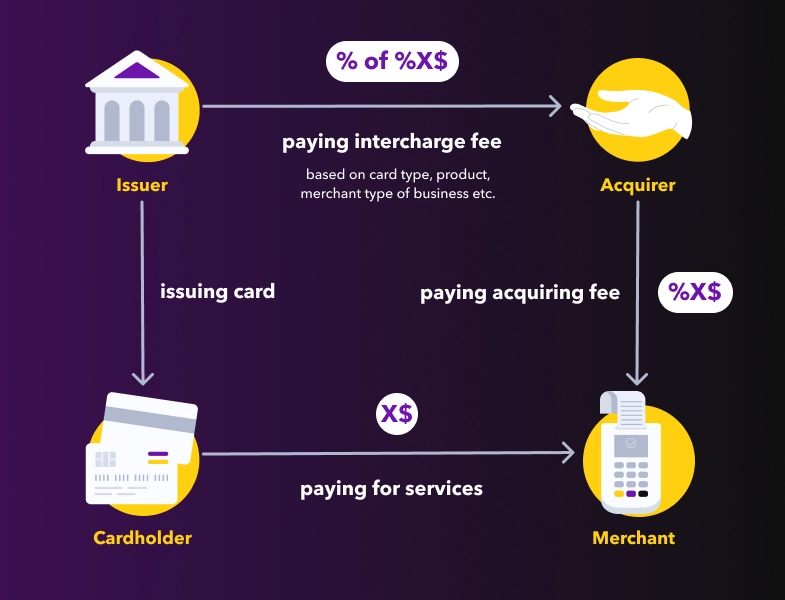
A three-party scheme may license third-party PSPs to carry out some issuing or acquiring activity (or both activities) while continuing to both issue cards and acquire transactions itself. For example, Amex operates a card payment system in which it undertakes its own issuing and acquiring. Amex also grants licenses to PSPs for issuing and acquiring.

Interchange Fee Regulation in the EU and in the United Kingdom keeps tabs on the interchange fees for major banks (0.2-0.3%) but omits smaller ones. That is why fintech tends to partner with minor banks for card issuing, to allow them to charge higher fees (generally, up to 2%).
An interchange fee may depend on several factors:
- Card type. Interchange fees for credit cards tend to be higher nowadays compared to debit cards.
- Marchant size and category. Gas stations usually pay less than supermarkets, and smaller merchants typically get higher rates.
- Transaction type. CNP transactions carry more risk than POS, so they often get higher interchange rates.
Through negotiations with a licensor, neobanks can push for better revenue conditions. For example, MasterCard agreed to share revenues from interchange fees with Revolut, though the latter does not publicly declare this fact. Revolut’s revenue through this model reached 95 million GBP (31% of its income).
Advantages of the interchange fee model:
- Stability.Though interchange fee consists of multiple commissions, the service provider usually receives a predetermined and stable percentage of transactions.
- Analytics. As a neobank, you can analyze customer behavior and spending categories to regulate pricing policies and bonuses for your clients.
Drawbacks of the interchange fee model:
- High regulation. As already mentioned, interchange fees are highly regulated, especially in the US and Europe, including the UK.
- Tough agreements. For high profit, you need to negotiate your percentage as a neobank with a card licensor, and it may prove to be quite a task for a new player.
- Dependency. The neobank itself cannot decide the amount of the interchange fee as it is settled by the government and licensors.
International Money Transfers
Since the rise of online banking, customers have discovered a much easier way of sending and receiving money. With the transfer market continually growing on an annual basis, people sent 713 billion USD worldwide in 2021 alone.
PayPal was a pioneer of this trend, and is still on track, with Wise (former TransferWise) being one of the successors to its legacy among neobanks. Actually, Wise took money transfers to a much more efficient level. Revolut, Monzo, and Starling Bank, also use this service in their business model.
Generally, the international money transfer model is based on a percentage fee of a sum transferred. The rate varies according to the transaction speed, destination country, time of day, and account type — private or business.
For example, Wise charges a fee for every money transfer, usually quite competitive. First, a customer picks the amount and currency, then sees the amount to be charged by the service provider. Currently, customers can send money in 50 currencies, some of which are available only in corresponding countries, totaling five billion USD a month in money transfers across 71 countries for Wise. Among other bonuses for its customers, the transfer provider keeps the exchange rate for 96 hours, so that its customers may avoid underpayment due to rate fluctuations.
All various ways to send money abroad may be simplified into three main categories:
- Bank account to bank account. This method uses customers’ banking information to identify and verify transactions. Evidently, both the sender and receiver should have accounts in corresponding currency and a service plan that enables use of SWIFT, SEPA, or similar systems.
- Online money transfer services. As with most digital products and services, customers use their email, phone number, or unique digital ID as a means of identification. In turn, service providers need to implement sophisticated data encryption and protection measures, including blockchain for crypto transfers.
- Remittance companies. This time-proven method of wiring money abroad uses senders’ and receivers’ names and procedural IDs to verify a transaction. Also, companies manage their day-to-day operations via agreements with existing banks, their branches, and employees.
Advantages of the IMT model:
- Wide geography. Customers can get comparable quality service in different countries, and both in large cities and small provinces, as money transfer only needs an internet connection. Physical branches for service providers are required no more.
- Customers’ autonomy. There is no possibility of payment reversals or chargebacks. As the transaction is facilitated between two subjects, the neobank isn’t involved and therefore cannot be accused of any kind of mistakes.
- Big market. Compared to other business models, IMT is a popular service with a more diverse audience, which means easier marketing strategizing and fewer risks.
Drawbacks of the IMT model:
- Exchange rate fluctuation. IMT contains a hidden fee due to the exchange rate, which fluctuates independently. So, while providing IMT service, you will be faced with a choice: to keep the exchange rate in favor of your customers and affect your income, or to make your clients uncomfortable.
Loans & Overdrafts
While similar in many aspects, loans and overdrafts still differ a bit.
Loan is a long-term money lending that is charged with interest and paid later by the customer, usually on a monthly basis. For lending money as a loan, a bank needs a special license which is not easy to get.An overdraft is an overrun of costs on the customer’s account, often with a grace period, and an interest fee charged upon its ending. For providing an overdraft service, a bank is enough to have an EMI license.
An EMI license is widespread among neobanks and challengers. But it means that licensee can only lend the amount of money they actually possess.
Though overdraft and loan fees might seem like relatively low sources of revenue for a bank, they still comprised 18% of Monzo’s total profit in 2020. Currently, Monzo charges up to 39% in overdraft fees for transactions with a negative balance, depending on the customer’s credit score and how many days they owe the bank.
As for the loans, Monzo allows borrowing money from the bank for any purposes. The annual percentage rate may reach up to 19.5% and the loan sum cannot rise above 15,000 GBP. The interest rate depends on the customer’s credit score likewise, as well as the borrowed amount and the payment schedule.
Our next challenger, Starling Bank, will charge an overdraft of 15 to 35 percent on the negative balance, depending on the customer’s credit score. Interest is accrued daily and charged on the 15th day of the following month. This bank also suggests to customers another way of using overdrafts: a customer may pre-arrange for an overdraft to receive a grace period as a bonus.
Other neobanks may not charge any fees for overdrafts but collect an additional compensation for missed credit card payments, e. g. Tandem charges 12 GBP. Speaking of Tandem, it also gives green loans with competitive rates for the purposes connected to reducing greenhouse gas emissions, which makes lending the third biggest source of its income.
Advantages of the loans & overdrafts model:
- Flexibility. As a bank, you may implement as many loan options as you wish and create alternative ones for customers on a negotiation basis. You may also change the overdraft rules whenever you deem it necessary, simply by informing your customers about it in advance.
- Predictable interest income. Regardless of the risks, you can still predict your interest income, especially using big data.
- Lower regulations for overdrafts. There are some regulations for credit lines and overdraft fees all around the world but they are still not well regulated, which means there are opportunities to raise income. The smaller banks and most credit unions are not even required to report their overdraft fee revenue at all.
Drawbacks of the loans & overdrafts model:
- Higher risks. The bank would be putting its own revenue at risk if loan and overdraft interest were not paid on time.
- Licensing. Most neobanks and challengers lend money by an EMI license. It means that they can only lend the amount of money they actually possess.
Instead of conclusion
Due to the speed and convenience of personal financial management services, neobanks and challengers are conquering the world. And though there is still a place in the market for new digital banks, the competition is getting tougher. Those who define their target audience and tailor their business model to meet their needs will gain a competitive edge.
Our Dashdevs team, with 7 years of experience in fintech, is here to help you deliver your unique financial product to your customers. We cover the entire process: from business modeling to software developing. We can guide you through analysis and development processes from scratch till the launch and further provide technical support. Already interested? Let’s talk, and subscribe to tune in to the fintech world!








