AI Credit Scoring Implementation: From Legacy Systems to Intelligent Lending
AI credit scoring is rapidly replacing traditional underwriting, delivering 15–25% better accuracy, real-time risk insights, and faster loan decisions. As legacy systems struggle with rising data complexity, regulatory demands, and new borrower behavior, AI has become a business-critical upgrade for lenders aiming to grow safely and competitively.
This article gives banking executives a clear roadmap for adopting AI-powered scoring—from evaluating models and integrating them into core systems to achieving measurable improvements in approval rates, default reduction, and operational efficiency.
Key takeaways:
- 15–25% more accurate risk prediction, enabling more approvals with fewer losses.
- Up to 60% lower manual workload through automated AI credit decisioning.
- Expanded lending to thin-file segments via alternative and behavioral data.
- 30% reduction in default rates thanks to adaptive, self-learning models.
- Smooth integration with legacy systems, helping banks quickly integrate AI/ML with banking workflows.
Why AI Credit Scoring Is Reshaping Modern Lending

Lenders across the world are quietly facing the same problem: traditional credit models can no longer keep up with how people earn, spend, and manage money today. Static scorecards were built for a world of stable jobs, predictable histories, and slow-changing financial behavior. That world no longer exists.
As digital payments, alternative employment models, and real-time financial behaviors grow, banks need tools that can read a much wider picture of a borrower’s life. This is where AI credit scoring steps in—and why adoption is accelerating across every major lending market and payment gateway.
AI isn’t just improving credit scoring—it’s expanding the universe of people you’re able to understand.
From narrow data to a fuller borrower profile
AI models analyze information that traditional scoring entirely ignores. Instead of relying only on bureau scores and an applicant’s past, AI looks at current behavior and real-time indicators, giving lending as a service a far more accurate and fair assessment.
Here’s the difference in simple terms:
| Traditional Scoring | AI-Driven Scoring |
| Limited historical data | Real-time financial behavior |
| Bureau-centric | Alternative + transactional data |
| Static rules | Adaptive learning |
| Thin-file = high risk | Thin-file = evaluable |
This expanded view is what enables banks to responsibly approve credit for young borrowers, freelancers, gig workers, and immigrants—segments long underserved by conventional credit systems.
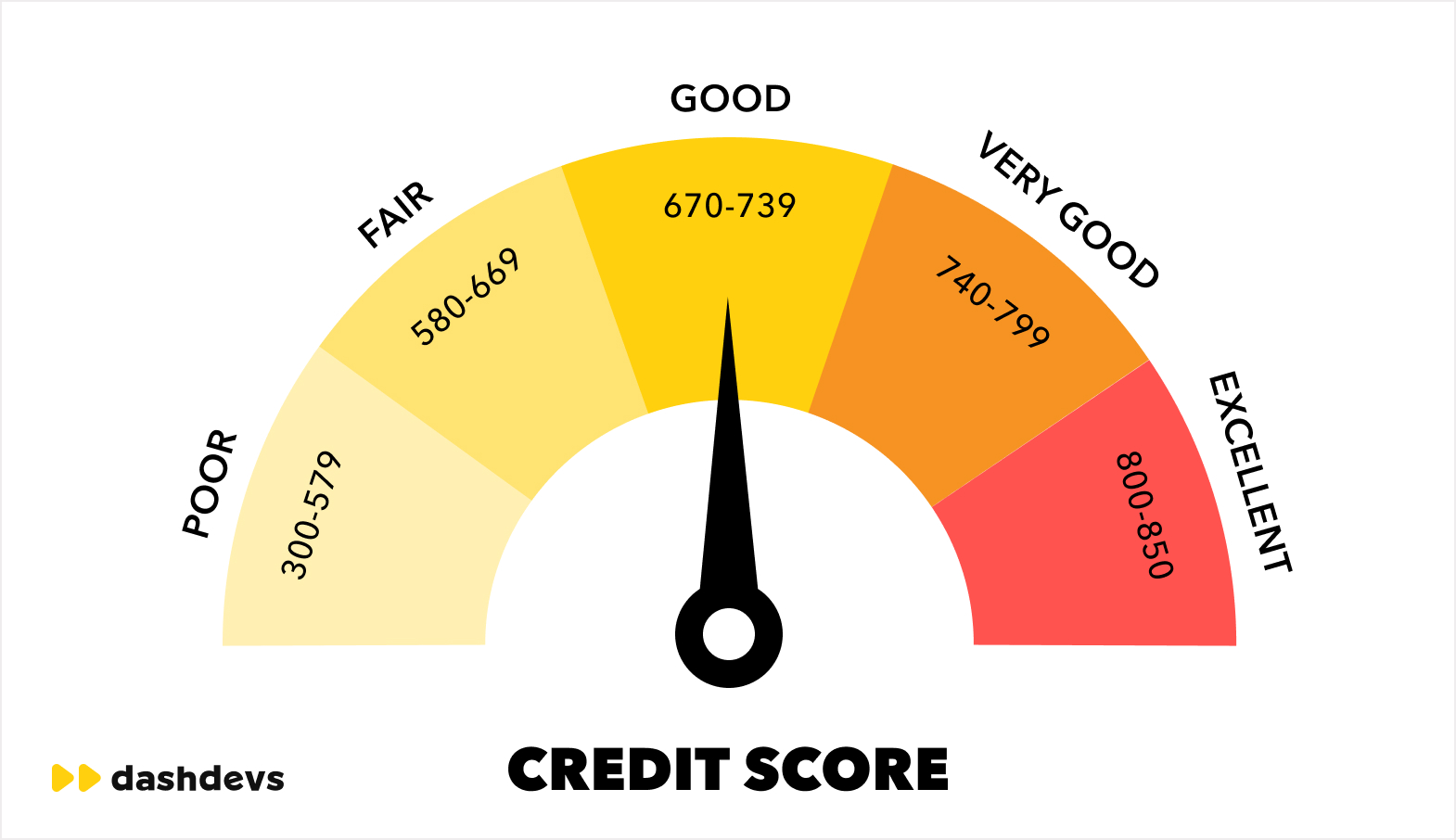
Speed and accuracy are now competitive advantages
Modern lending isn’t just about better risk prediction—it’s about doing it faster. AI-powered assessment reduces manual review, automates document checks, and delivers decisions in minutes. The result is a clearer, faster path from application to approval.
Industry projections show the pace of change:
- AI could save the global banking sector over $1 trillion by 2030.
- AI-driven credit scoring is expected to grow 67%, reaching $44B by 2028.
Lenders are adopting AI not because it’s trendy, but because it solves operational bottlenecks, cuts losses, and dramatically improves the customer experience.
With up to 85% higher accuracy, continuous model learning, and data-driven fairness controls, AI is reshaping how institutions measure risk. The move away from static scorecards isn’t theoretical—it’s happening right now across retail, SME, embedded, and BNPL lending.
In the next section, we’ll break down how AI models actually work and what it takes to implement them inside a legacy banking environment.
How AI Credit Scoring Works: From Raw Data to Real Decisions
AI credit scoring is built on a simple idea: The more you understand about a borrower’s real behavior, the better your credit decisions become.
To do that, AI models take thousands of signals—financial, behavioral, and transactional—and map them to outcomes like repayment likelihood, early delinquency risk, or fraud probability. This creates a far richer risk profile than any rule-based scorecard can produce.
The process can be explained as a simple progression:
Better data → Smarter models → Clearer decisions → Stronger outcomes
Let’s walk through each stage in the order that it happens inside a modern lending engine.
Step 1: Expanding the Data Universe
“Even the two most widely used scoring frameworks—FICO and Vantage—rely on similar, limited data sources. AI expands this dramatically.”
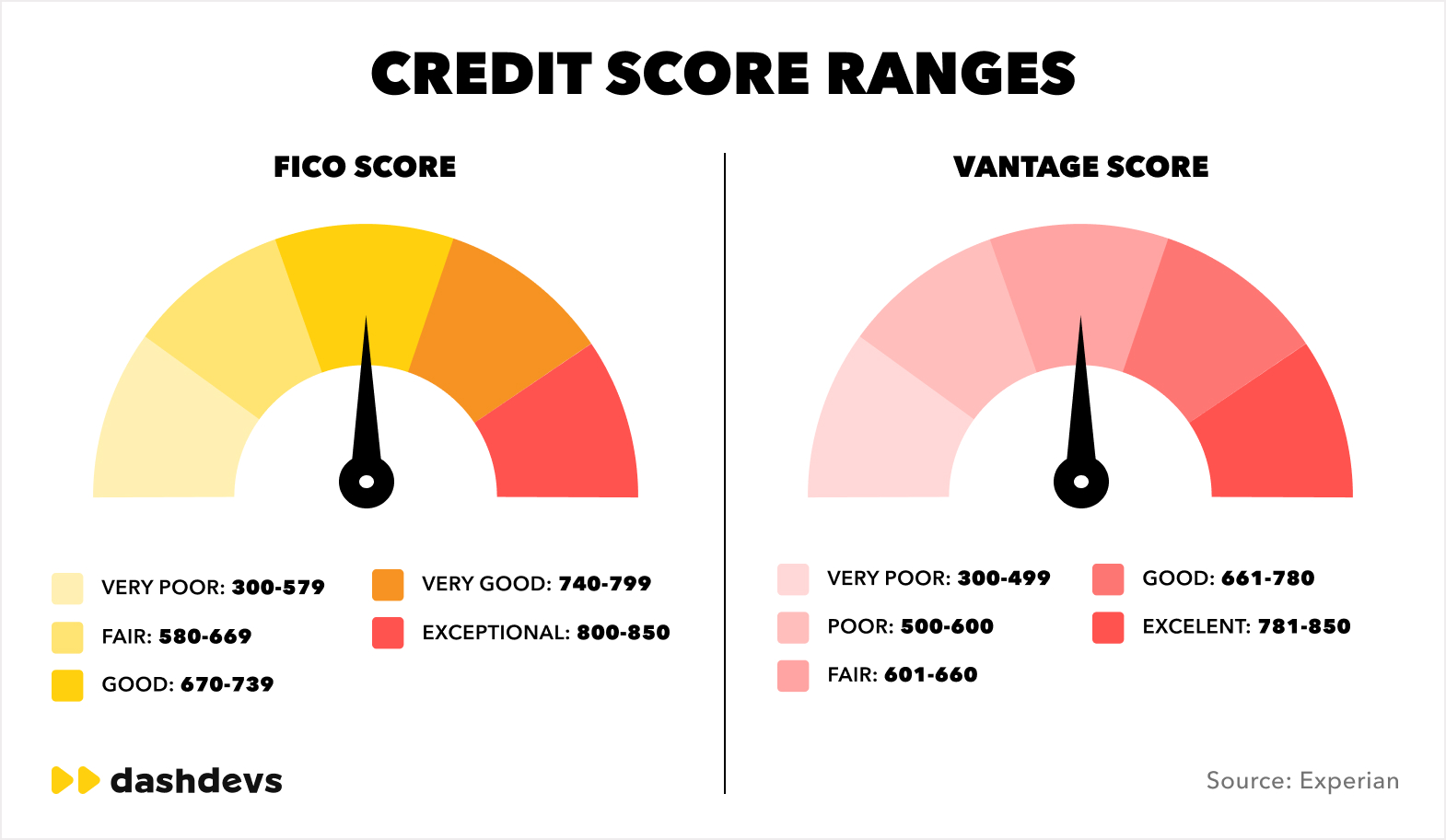
The biggest breakthrough of AI isn’t the algorithm. It’s the ability to finally see the full financial picture.\
AI systems pull thousands of signals to build a complete profile of a borrower’s behavior today—not just their past.
Types of data used by AI models
| Data Type | Examples | Why It Matters |
| Transactional data | Spending behavior, cash flows | Predicts liquidity stress and repayment ability |
| Utility & recurring payments | Rent, telco, subscriptions | Reliable proxy for financial discipline |
| Open banking data | Real-time account activity | Reduces dependency on bureau-only scoring |
| Device & identity data | IP history, login patterns | Links credit risk with fraud detection |
| Behavioral indicators | Payment timing, spending rhythms | Highlights stability vs volatility |
This richer dataset sets the foundation for a far more accurate scoring process.
Step 2: Transforming Data Into Meaningful Signals
Raw data alone is not enough. AI systems must convert it into structured insights—called features—that models can learn from.
This process is known as feature engineering, and in credit risk, it’s the true competitive advantage.
Examples of high-impact features
- Income volatility across 30/60/90-day windows
- Ratio of essential vs. discretionary spending
- Payment consistency (on-time %, weekends vs weekdays)
- Surplus cash after mandatory obligations
- Merchant category concentration
- Number of overdraft-like events per month
These signals give AI a deep understanding of borrower behavior—something no traditional scorecard can replicate.
Your model is only as good as your features. If the signals are strong, the predictions will be too.
Once these patterns are extracted, the model can begin learning.
Step 3: Machine Learning Models Predict Future Risk
With rich, structured features in place, AI models can analyze how certain patterns correlate with repayment outcomes.
Instead of static rules, the model learns from historical performance and adapts to new behavior over time.
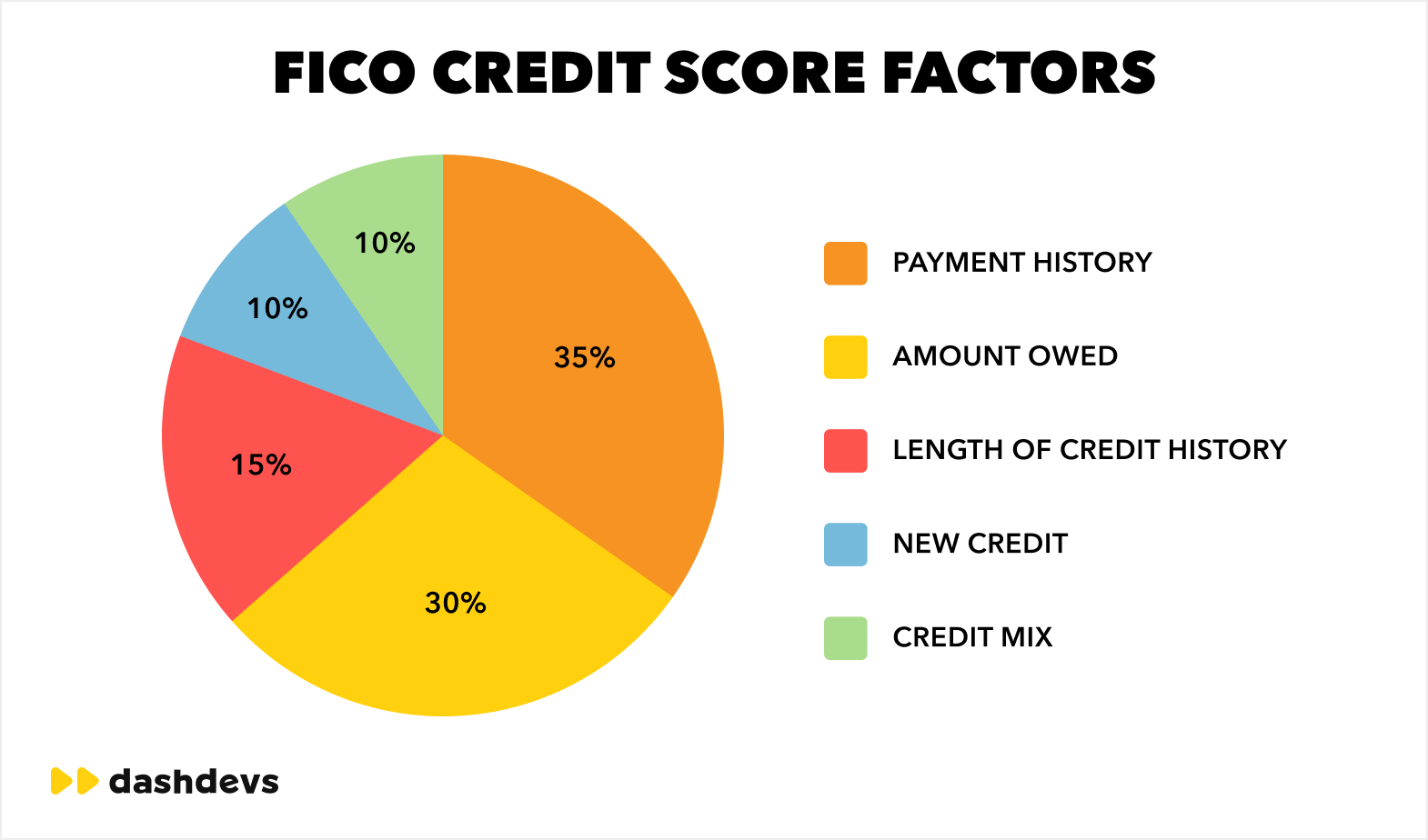
Common models used in AI credit scoring
- Gradient Boosting Models (XGBoost, LightGBM)—fast, accurate, and explainable
- Neural Networks—ideal for large, complex transaction sets
- Hybrid logistic regression—regulatory-friendly, used with enhanced ML features
- Ensemble models—combining algorithms for higher stability
The model outputs a probability of default, early delinquency, or approval readiness—usually in milliseconds.
And unlike scorecards, which remain unchanged for years, AI updates continuously as it sees new borrower behavior.
Step 4: Turning Predictions Into Real Decisions
AI doesn’t replace credit policy—it enhances it. The model’s prediction flows into the lender’s decision engine, where business rules and compliance requirements are applied.
Decision engine components
- Approval/decline thresholds
- Risk-based pricing
- Limit assignment
- Exceptions & manual review rules
- Fraud flags and identity checks
- Region-specific regulatory constraints
This ensures AI stays aligned with lending policies and regulatory frameworks while still delivering superior accuracy and speed.
Step 5: Explainability and Compliance Close the Loop
A key requirement in modern lending is transparency. Banks must be able to explain why a customer was approved or rejected.
Explainable AI (XAI) tools provide clear, regulator-ready insights:
- Top factors influencing each decision
- Fairness & bias checks
- Comparison between applicants
- Counterfactual explanations (“What would change the outcome?”)
Common XAI tools
- SHAP
- LIME
- Decision breakdown charts
- Sensitivity analysis
These tools protect institutions from bias claims and build customer trust in automated systems.
By following these five steps—data → features → models → decisions → explainability—AI credit scoring delivers measurable results:
- Up to 85% higher accuracy
- Faster approvals (minutes instead of days)
- Lower default rates
- Better segmentation across customer groups
- Expanded access for thin-file borrowers
This isn’t theoretical. It’s already happening across retail lending, SME financing, BNPL, and embedded finance.
In the next section, we’ll look at the implementation roadmap—how institutions integrate AI scoring within legacy systems without disrupting daily operations.
Implementation Roadmap: How Banks Integrate AI Credit Scoring Into Legacy Systems
Even when executives understand the value of AI credit scoring, one concern almost always comes next:
“How do we implement this without breaking everything that already works?”
The reality is encouraging:
AI credit scoring doesn’t require replacing your existing LOS, core banking system, or risk infrastructure. Instead, it slots into what you already have—modernizing your decisioning layer without forcing a full architectural rewrite.
Successful AI adoption is never a big bang. It’s an evolution built on small, measurable integrations.
Below is the step-by-step roadmap DashDevs uses with clients across Europe, North America, and the GCC. Each phase builds naturally on the previous one, reducing implementation risk and ensuring compliance from day one.
Step 1: Assess Your Current Risk Engine & Data Readiness
Before any model is trained, lenders must evaluate:
- What data is available (transactions, bureau, open banking, behavioral signals)
- How clean and structured that data is
- Which decisions are automated vs manually reviewed
- What regulatory expectations apply (EU AI Act, GCC credit bureaus, US ECOA/FCRA)
- Where the biggest pain points are (thin-file approvals, fraud leakage, TAT delays)
This creates a baseline understanding of where AI can deliver the fastest impact.
Example output of a readiness assessment
| Category | Current State | AI Opportunity |
| Data sources | Bureau + bank statements | Add cash flow analysis, device intelligence |
| Manual reviews | 40–60% | Reduce to <10% with automated triage |
| Fraud checks | Rule-based | ML-based anomaly detection |
| Turnaround time | 3–48 hours | Decisioning in minutes |
This assessment avoids “AI for AI’s sake” and anchors the initiative to measurable improvements.
Step 2: Build the Data Pipeline & Feature Store
As explained in Section 2, AI models are only as strong as the features they learn from. This is why the data pipeline becomes the backbone of the entire system.
What this phase includes:
- Ingesting data from core banking, LOS, open banking, and external APIs
- Standardizing and cleaning raw inputs
- Creating real-time and batch data flows
- Engineering behavioral, transactional, and cash-flow features
- Storing features in a reusable “feature store” for future models
This is where institutions begin to move from static, historical scoring to dynamic behavior-based risk modeling.
Once you have a strong feature pipeline, every future model becomes 10× easier.
Step 3: Train, Validate, and Stress-Test the Model
With your features ready, the next phase is designing and training the model itself—typically using a combination of:
- Gradient boosting (LightGBM, XGBoost)
- Ensembles
- Neural networks (for high-volume transactional lenders)
What’s included in this phase:
- Splitting data into training/validation sets
- Testing for accuracy, stability, and bias
- Benchmarking against your current risk engine
- Simulating real-world lending performance
- Calibrating thresholds for risk bands
A well-trained model should show:
- Higher approval rates
- Lower false negatives (good borrowers incorrectly rejected)
- Lower false positives (high-risk borrowers approved)
- Better segmentation across customer types
- Stability across economic cycles
If these benchmarks aren’t clear, the model isn’t ready.
Step 4: Deploy the Model Into Your Lending Workflow
This is the moment AI begins to work inside your production environment—quietly and safely.
Deployment often includes:
- API integration into LOS or customer onboarding apps
- Real-time scoring endpoints
- Rule-based overrides for compliance
- Automated triage to reduce manual reviews
- Fraud flags embedded into the decision engine
A typical flow looks like this:
- User submits an application
- Data sources connect (banking data, bureau, document verification)
- Features are calculated in real time
- The model generates a risk score
- Business rules interpret the score
- The decision engine outputs approve/decline/review
This phase often produces the earliest wins: shorter decision times, fewer manual reviews, and clearer approval logic.
Step 5: Add Explainability, Monitoring & Governance
AI scoring cannot operate without ongoing governance. This is both a compliance requirement and a business necessity.
Institutions must monitor:
- Model drift (when accuracy declines)
- Fairness and bias metrics
- Approval & decline consistency
- Performance across demographic segments
- Economic sensitivity (stress testing)
Explainable AI (XAI) frameworks—like SHAP and LIME—are embedded to ensure transparency.
What XAI provides:
- Top factors influencing a decision
- Counterfactual explanations (“what would change the outcome?”)
- Clear reasoning for auditors and compliance teams
- Evidence of fairness
You don’t build an AI model—you build an AI lifecycle. Monitoring and governance matter as much as accuracy.
Step 6: Iterate Quickly and Scale
Once AI scoring is live, lenders can expand it into:
- Credit limit assignment
- Risk-based pricing
- Collections prioritization
- Early delinquency prediction
- Fraud detection Most institutions treat the first model as Phase 1—then grow into a full AI risk platform over 6–18 months.
| Phase | What Happens | Outcome |
| 1. Assessment | Evaluate data, workflows, risks | Clear AI opportunity map |
| 2. Data Pipeline | Build inputs & feature store | Strong foundation for modeling |
| 3. Model Training | Train, test, calibrate AI model | Higher accuracy & fairness |
| 4. Deployment | Integrate into LOS & decision engine | Faster, automated approvals |
| 5. Governance | Explainability, monitoring | Compliance-ready AI scoring |
| 6. Scaling | Expand into pricing, limits, collections | Full AI-driven risk lifecycle |
Conclusion
AI credit scoring is no longer a future trend—it has become the core infrastructure for modern lending. As borrower behavior evolves, traditional scorecards and rule-based models struggle to keep pace, creating blind spots that impact approval rates, risk accuracy, and overall portfolio performance. AI closes these gaps by analyzing richer data, learning from real-time patterns, and delivering decisions that are faster, fairer, and significantly more predictive.
For lenders, the transformation isn’t about replacing the old with the new. It’s about enhancing existing systems with intelligent decisioning layers that integrate smoothly into established workflows. When implemented responsibly—with strong data foundations, transparent governance, and clear monitoring—AI becomes a strategic advantage rather than a technical experiment.
Early adopters are already seeing the results:
- Higher approval rates without increasing risk
- Lower default rates through proactive detection
- Faster turnaround times that reduce operational costs
- Better access for thin-file and underserved borrowers
And this is only the beginning. As regulations mature and digital ecosystems expand, AI-enabled credit decisioning will define which financial institutions stay competitive and which fall behind.
DashDevs helps financial institutions design, build, and integrate AI-driven scoring engines that are accurate, explainable, and regulator-ready from day one.
Let’s talk about upgrading your lending strategy with intelligent decisioning.

