Understanding Cross Border Payments, Transactions, and Money Exchange
In 2026, running an international business without cross-border payments is simply impossible. Global trade, digital platforms, and financial institutions rely on seamless cross-border transactions to move money across countries and currencies in real time.
The volume of cross-border payments continues to grow, with global cross-border transactions already exceeding $190 trillion annually and rising as businesses scale globally. Yet despite their importance, cross-border payment flows remain complex—affected by fees, FX costs, regulations, and fragmented infrastructure.
In this article, we explain how cross-border payments work, walk through a typical cross-border transaction, and explore modern cross-border payment solutions that help businesses execute cross-border payment flows faster, more transparently, and at scale.
What Are Cross-Border Transactions and Money Exchange?
Cross border transactions are financial transfers between parties located in different countries. They typically involve currency exchange, international banking infrastructure, and regulatory controls. In simple terms, any movement of money between accounts registered in different jurisdictions qualifies as a cross border transaction—one of the most common forms of global financial interaction today.
This scale is significant: global cross border payment volumes exceeded $190 trillion annually, reflecting how deeply international transactions are embedded in modern business and consumer activity.
Money exchange refers to the process of converting one currency into another, usually through a bank, payment provider, or currency exchange service, based on prevailing exchange rates. Because cross-border transactions often involve parties using different national currencies, currency conversion is a core component of nearly every cross border payment.
Within the cross border payment process flow, currency exchange ensures that transferred funds arrive in a form that is usable in the recipient’s country. This process enables value to move seamlessly across borders while complying with local currency standards, financial regulations, and settlement rules—making international payments functional, compliant, and economically meaningful for both parties.
How Do Cross-Border Payments Work?
While the mechanics of cross-border payments follow a standard flow, real-world execution depends heavily on product architecture, regulatory exposure, and transaction volume. DashDevs has implemented cross-border payment solutions across consumer banking, investment, and hospitality platforms—including Dozens, iOL Pay, and Chip.
Below is how the cross-border payment process flow works in practice, illustrated through these projects.
Transaction initiation
A cross-border payment starts when a user initiates a transfer via a bank or payment provider, entering recipient and transaction details. In Dozens, a UK challenger bank, DashDevs designed secure payment initiation flows that support international transfers while enforcing user limits, account controls, and real-time validation—critical for regulated cross-border transactions in retail banking.
Currency conversion
If the transaction involves different currencies, FX conversion is applied based on provider rates.
For Chip, a savings and investment app, DashDevs integrated FX logic that ensured transparent currency conversion and predictable outcomes for users funding accounts or moving money internationally—an essential requirement for trust in cross-border money transfer and investment products.
Transfer of funds
Payment instructions are routed through international rails such as SWIFT or local clearing systems. In Dozens, DashDevs helped architect payment routing that balances speed and reliability across multiple corridors, ensuring consistent execution of cross-border business payments even during peak loads.
Intermediary banks involvement
If no direct relationship exists between sending and receiving banks, intermediary banks relay the funds. In the iOL Pay hospitality payment solution, DashDevs optimized the transaction chain to reduce unnecessary intermediaries—lowering fees and improving settlement times for merchants handling frequent cross-border transactions from international guests.
Compliance checks
Every cross-border transaction is screened for AML, KYC, and CTF compliance.
Across Dozens, IOL Pay, and CHIP, DashDevs embedded compliance checks directly into payment flows. This approach reduced transaction delays, simplified audits, and ensured regulatory alignment without disrupting the payment experience.
Funds received by the recipient’s bank
Once cleared, the recipient’s bank accepts the payment and finalizes any remaining FX conversion. For IOL Pay, predictable acceptance timing was especially important to support daily reconciliation and cash-flow planning for hospitality businesses operating across borders.
Final settlement
The recipient’s account is credited, completing the cross-border payment.
In all three projects, DashDevs ensured the final settlement integrated seamlessly with reporting, accounting, and reconciliation systems—an often underestimated requirement in scalable cross-border payment platforms.
You can review the visualization of the cross-border payment process flow, structured by parties involved in the infographics below:
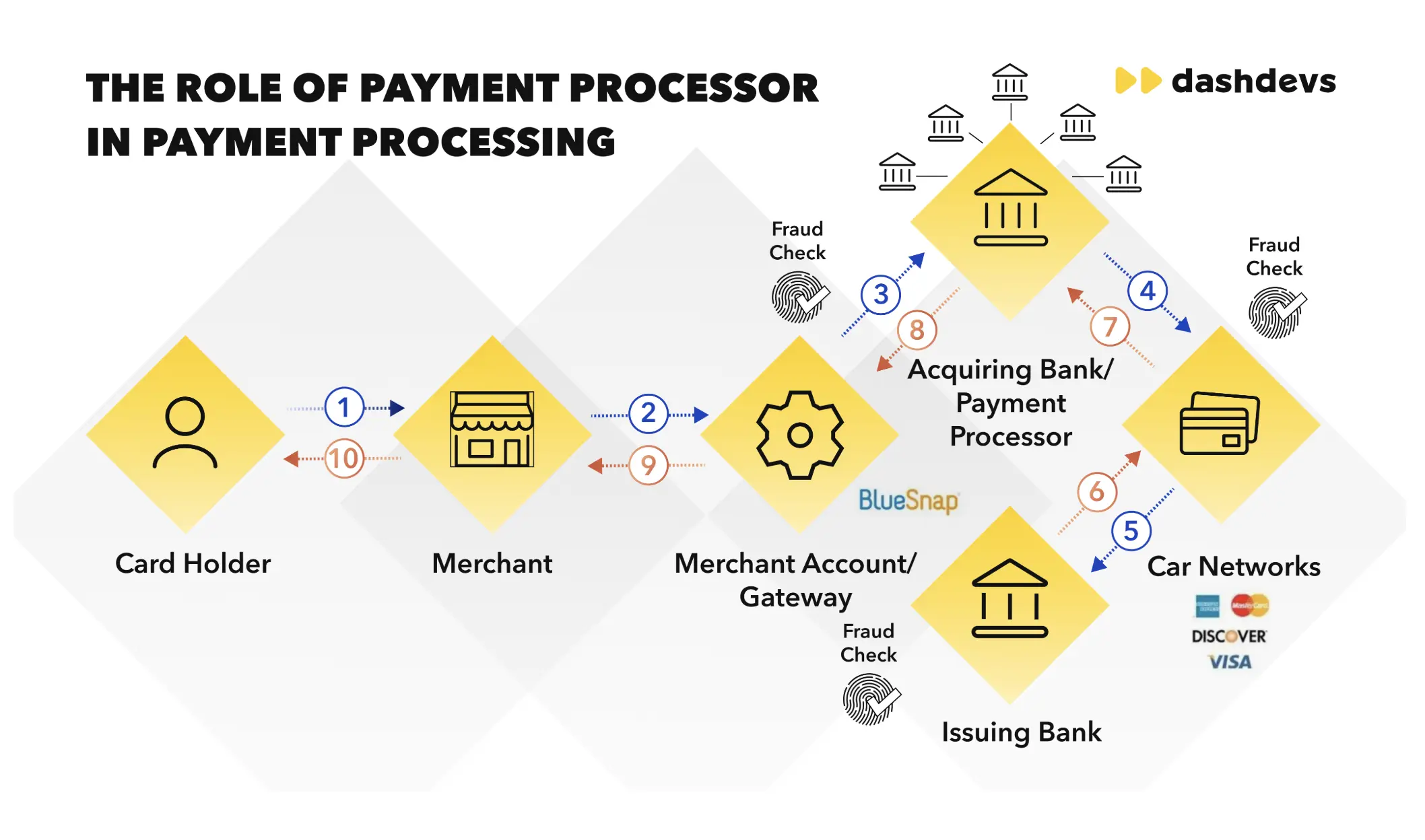
Other considerations related to cross-border money transfer are:
- Fees and charges
Cross-border payments often incur fees, including cross-border transaction costs, service charges, and potentially intermediary bank fees. These costs vary by provider and transaction type.
Businesses must consider these fees for cost-effective transactions, as they can significantly impact the total cost, especially for frequent or high-volume transactions.
- Exchange rate fluctuations
Currency exchange rates can fluctuate dramatically, influencing the cost and value of transactions.
Businesses that make cross-border payments must regularly monitor exchange rates and may employ hedging measures to reduce the risks associated with these swings, ensuring budget predictability.
- Delivery time
The time it takes for cross-border money transfers to be processed and cleared can vary widely, from the same day to several days, depending on the payment method and both the sending and receiving countries’ banking systems.
Since timely execution is crucial for maintaining cash flow and operational efficiency, it’s important to ensure the proactive transfer of funds.
- Bank and country-specific restriction
Different countries and banks have varying regulations and restrictions on cross-border payments. These include the above-mentioned AML and CMF laws. Besides, they may include transaction limits, sanctions and embargos, indicating the purpose of payments, and providing invoices, contracts, or other proofs of the transaction’s legitimacy.
Understanding and complying with these regulations is essential to avoid delays or rejections of transactions, which can be critical in time-sensitive business operations.
- Payment method availability
The availability of different payment methods, like wire transfers, international ACH, or digital payment platforms, varies by country and by the provider of banking services.
Businesses must consider which methods are both accessible to them and to their partners and customers. It’s also important to balance factors like cost, convenience, security, and speed to select the most suitable payment method.
What Are the Types and Methods of Cross-Border Payments?
It’s important to understand that there are distinct types of international payments, varied by the parties involved and the purpose of transferring funds. It’s often the case that different laws and regulations are imposed on different types. Besides, while some cross-border payments may be nearly-instant, others can take banks up to a business week to conduct.
Common types of sending cross-border payments are:
- Business-to-Business (B2B) transactions. These involve transfers between businesses in different countries. B2B transactions are often large in volume and value, used for purchasing goods, services, or fulfilling contractual agreements.
- Consumer-to-Business (C2B) transactions. This type refers to payments made by individuals to businesses in another country. It’s common in e-commerce, consumers purchase goods or services from overseas companies.
- Business-to-Consumer (B2C) transactions. B2C transactions occur when businesses send payments to individual consumers abroad. This can include refunds, payments for freelance services, or direct sales.
- Consumer-to-Consumer (C2C) transactions or Peer-to-Peer (P2P) transactions. One of the examples of C2C cross-border transactions is cross-border remittance, i.e., transferring personal funds from an individual to an individual in another country.
Now, let’s proceed with reviewing the exact cross-border payment methods that can be offered by financial institutions to conduct your transfer:
- International wire transfers. Swiftly and securely transfer funds between banks globally using the SWIFT network. Ideal for large, urgent transactions, but typically involves higher fees and requires the recipient’s bank details.
- International money order. Purchase a money order and send it overseas for the recipient to cash or deposit. International money orders are considered a secure method, but they’re comparatively slower and less convenient, so they’re often used when other electronic methods aren’t available or preferred.
- International ACH. Automated Clearing House (ACH) transfers funds electronically between banks, suited for regular, smaller payments like payroll. It’s cost-effective but slower than wire transfers, with varying processing times depending on the countries involved.
- Prepaid debit card transactions. This method implies loading money onto a prepaid debit card, which the recipient can use for purchases or withdraw cash. It’s convenient for regular remittances, and it offers easy access to funds, but may involve loading and withdrawal fees.
- Online money transfer. Online transfer of funds are basically done using online platforms or apps. Fast, convenient, and often cheaper than traditional banking methods. Cross-border money transfers are ideal for personal remittances and small business transactions, with varying fees and exchange rates.
- Paper checks. It’s a traditional method involving sending a check by mail, which the recipient deposits in their bank. Less popular due to slower delivery, the risk of loss or theft, and the availability of faster electronic methods.
There are also alternative cross-border payment services, including:
- Digital wallets. In cross-border payments, digital wallets enable electronic storage and transactions of multiple currencies, offering quick, convenient international transfers and payments through mobile or online platforms.
- Cryptocurrency transactions. Cryptocurrency transactions in cross-border payments allow for direct, decentralized, and often faster transfers across borders without the need for traditional banking systems or currency conversions.
Guide your choosing of the cross-border payment platform and method based on their accessibility to both parties involved, turnaround times, convenience of conducting, and transaction fees involved.
We should also mention Foreign Exchange (Forex). It’s not an international payment service but rather a component of cross-border payment flow that enables money exchange. It can be defined as follows:
Forex is a global marketplace that enables the conversion of one currency to another.
Forex operates through a network of banks, corporations, brokers, and individuals trading one currency for another and can be integrated as a component in a system for settling international transactions with local currency values.
Why Use Cross-Border Payments: Key Benefits
Without elaborating on the obvious necessity to conduct cross-border transactions should you need to transfer funds globally, here are the business reasons to establish solid ways of transferring funds abroad or receiving them:
- Mobile device invoice payments anytime
Some methods of international transactions allow for the settlement of invoices anytime, anywhere, using a smartphone or tablet. The flexibility offered by mobile payments is crucial for businesses with global operations, enhancing convenience and efficiency. It eliminates the need for physical banking infrastructure, enabling swift payment processing even on the go.
- Automate intelligent payment scheduling
Cross border payment systems can automate payment scheduling, ensuring timely transactions while minimizing manual intervention. This feature is especially valuable for businesses with regular international payments, such as payroll or supplier invoices, as it reduces the risk of delays and errors, enhancing operational efficiency.
- Expand global market presence
Utilizing cross-border payments facilitates easier entry into international markets. Businesses can smoothly transact in multiple currencies and adhere to local financial practices, making it easier to expand operations and reach new customers globally, contributing to business growth and increased market share.
- Boost competitive advantage
Offering seamless cross-border payment options can distinguish a business from its competitors. It demonstrates a commitment to catering to international clients and suppliers, enhancing customer satisfaction. This capability can be a deciding factor for clients choosing between companies in a globally connected market.
- Increase the number of suppliers and affiliates
The ability to efficiently handle cross-border payments widens the pool of potential suppliers and affiliates. Businesses are not limited by geographic boundaries, enabling them to source the best products, services, and partnerships worldwide, often at more competitive rates, thereby optimizing their supply chains and affiliate networks.
The big idea here is that for a business operating globally, there is no way to go without international transfers. The only difference is that you can pick the most convenient cross-border payment companies as well as the necessary forms and suitable methods to conduct transactions.
The List of Cross-Border Payment Providers
To become a participant in a foreign exchange and payment system, you need to partner with one of many providers of money transfer solutions. The list of the most reliable and well-established vendors for choosing include:
- PayPal. A global online payment system that facilitates cross-border payments and currency conversions for both individual and business users.
- Wise (formerly TransferWise). This foreign exchange financial technology company offers transparent, low-cost international money transfers using real exchange rates, popular among individuals and businesses.
- Western Union. This money transfer leader provides a well-established service for international money transfers, accessible online, via mobile apps, or through physical locations.
- Currencycloud. This Visa’s solution provides a platform for businesses to manage cross-border payments and currency conversions with API-driven solutions.
- Revolut. It’s a digital banking service offering global spending and international money transfers without hidden fees, including multi-currency accounts.
- OFX. This money transfer company specializes in international money transfers and foreign exchange, offering competitive rates and low fees for both individuals and businesses.
- Fixer. It’s an API service that provides real-time exchange rate data for global currencies, used in international financial applications.
- XE Money Transfer. Known for online foreign exchange tools, including their online currency converter application, XE Money Transfer offers international money transfers with competitive rates and low fees.
- Xignite. This provider offers financial and market data APIs, including ones designed to enable real-time and historical foreign exchange rates for financial institutions and fintech companies.
- Payoneer. It’s an online service for freelancers, online sellers, and businesses, enabling efficient receipt of international payments.
Guide your choosing with the availability of service for your region, transaction fees, convenience of usage, and other factors significant to your business. You can discover additional information about fintech integrations and providers from another our blog post.
Key Challenges for Cross-Border Payments and Solutions to Them
In over 12 years, DashDevs has helped multiple customers worldwide implement cross-border payment technology in their digital products. We have faced limitations of international payment that can result in pitfalls like overdue payments, transaction errors, and high fees if not addressed timely. That’s why we provide you with these challenges of cross-border payments and tried and tested solutions to them:
Cost Complexity
What is it: High fees and hidden costs are common in cross-border payments due to intermediaries and complex banking processes.
How to solve it: Look for transparent pricing models and trustworthy providers.** **Alternatively, utilize fintech cross-border payments solutions like blockchain or peer-to-peer platforms, as they reduce the number of intermediaries, thereby lowering costs.
Regulatory Compliance
What is it:
- Regional regulations governing transactions within specific areas, addressing local financial practices and cross-border interactions.
- National regulations which are country-specific laws controlling financial transactions, banking practices, and foreign exchange.
- Transaction-specific regulations which are specific rules applied to certain types of transactions, considering purpose, amount, or parties involved.
How to solve it: It’s not like there is a particular solution to all the complexities involved with meeting regulations. You just must be aware of the restrictions they impose for your transactions to stay compliant. Partnering with experienced financial service providers or using software that automatically updates with regulatory changes can aid in compliance.
Lack of Transparency
What is it: Lack of transparency refers to the difficulty of tracking the progress of payments and understanding the various fees and exchange rates applied.
How to solve it: Opt for payment platforms offering real-time tracking and detailed breakdowns of fees and rates. Blockchain technology can also offer greater transparency throughout the transaction process.
Security Threats
What is it: Risks like data breaches, fraud, and cyber-attacks due to the involvement of multiple parties and complex transaction processes.
How to solve it: As a service provider, establish robust security protocols such as advanced encryption, multi-factor authentication, and continuous monitoring of transactions. As a customer, opt for payment service providers that prioritize security and are compliant with international standards like PCI DSS.
Currency Exchange Rate Fluctuations
What is it: Fluctuating currency exchange rates can significantly affect the cost and value of cross-border transactions
How to solve it: In case you have your own payment processing system in place, then establish robust security protocols, including encryption, multi-factor authentication, and continuous monitoring. Alternatively, choose financial institutions or payment platforms with strong security reputations and compliance with international security standards.
Slow Processing Times
What is it: Cross-border payments can be slow due to the involvement of multiple banks and the need for currency conversion and compliance checks.
How to solve: Utilizing faster payment methods like SWIFT GPI or digital currency transactions can speed up processing. If such options are available at your provider, of course. Also, working with banks and providers known for efficient processing in relevant regions can help.
Final Take
For businesses and individuals alike, the real challenge is not executing international transactions, but understanding how different cross-border transactions work, where friction and risk emerge, and how to design payment flows that are secure, transparent, and scalable.
As transaction volumes grow, the effectiveness of your cross-border payment infrastructure directly affects cost control, operational resilience, and speed to market. Building or integrating cross-border payment systems therefore requires more than connectivity—it demands deep expertise across compliance, FX, settlement, and technology.
If you’re assessing how your cross-border payments are structured today—or planning to evolve them as your business scales—expert guidance can help clarify the next steps. Book a direct call with our team here.

