MARCH 18, 2024
11 min read
Whether you’re a fintech or a non-fintech business owner, you cannot overlook the rapid integration of banking services into platforms, services, and products from other industries. It’s commonly known as embedded finance.
The size of the embedded finance market in 2023 is estimated at 66.3 billion U.S. dollars and was forecast to grow at a CAGR of 16.5% over the next decade. It can be stated that nearly two-thirds of merchants consider their e-commerce platform a higher-tier finance service partner ahead of traditional banks. And that’s quite the insight into how rapidly technology tends to take over the finance sector.
Hardly embedded finance replaces traditional distribution channels of financial services, i.e., banks. Nevertheless, it’s useful to have a clear understanding of how embedded finance will impact your business, what benefits and challenges it may bring, what product offerings are on the market, and how you can take advantage of this innovative technology. Read this article for an in-depth insight into all the listed.
The Role of Embedded Finance Adoption
It’s safe to claim that the world is becoming increasingly digitalized. Respectively, businesses have to keep up with the tempo by adopting innovations that are not in the last place.
We can define embedded finance technology’s role in fintech and non-fintech sectors as follows:
- Embedded finance in fintech: A natural modification of traditional finance processes and an opportunity to ensure cross-collaboration with industries that used not to get involved with finance at all.
- Embedded finance in non-fintech: A simplification of finance-related processes, such as receiving payments for goods. Besides, it’s an additional opportunity to provide an extra service and ensure a higher-tier user experience for customers.
Embedded finance redefines how industries interact with and benefit from financial services. It provides individuals with a seamless buyer or user experience that cannot be interfered with by the constraints of traditional financial services. Embedded finance is one of the major trends of the year 2024 in the fintech industry. It represents a future where finance is not just a standalone sector of the economy but an integrated component of diverse digital ecosystems.
If you are curious about other key trends in banking to follow, check out another blog post by DashDevs.
What Is Embedded Finance and How It Differs from Traditional Distribution?
Let’s get down to obtaining a clear understanding of embedded finance compared to traditional distribution:
Embedded finance is the integration of financial services into non-financial products, platforms, and business ecosystems.
Embedded finance offers financial products outside of traditional financial service providers like banks or credit unions. It brings an exciting opportunity for customers to exploit all the financial capabilities, even when they request services from non-fintech firms. On the contrary:
Traditional financial service distribution is the provision of financial services under the supervision of a license holder, i.e., a conventional financial institution.
Without further ado, you can discover more about how traditional banking and embedded finance approaches correlate and what are the roles involved from the infographics below:

Source: PwC
Embedded finance vs. banking as a service is not exactly the rivalry. After all, 70% of executives in fintech claim that embedded capabilities are either core or complementary to their businesses.
How Do Embedded Financial Services Work?
As detailed previously, the use of embedded systems implies the inclusion of fintech solutions in non-fintech platforms or applications. From a technical perspective, the flow of adopting embedded finance includes the following steps:
#1 Conducting API integration
A financial service provider offers you an Application Programming Interface (API). You integrate the API into your application or platform, which often requires programming skills to set up proper authentication, make API calls, etc.
#2 User Interface (UI) and Experience (UX) designing
While the embedding financial services provider might offer basic UI components, you still may need to design its interface for a seamless user experience. This may involve embedding widgets, creating dashboards, or designing custom workflows.
#3 Ensuring data flow and management, as well as data handling compliance
Embedded finance solutions typically involve the exchange of sensitive financial data.
This requires setting up secure data transmission channels, ensuring customer data privacy, and standard compliance with GDPR, HIPPA, etc.
#4 Transaction handling
Depending on the financial service, e.g., payments or loans, the embedded system may need to handle various transaction states such as pending, completed, failed, etc. Having proper error handling, retries, and fallback mechanisms in place here is crucial to ensure a smooth end-user experience.
#5 Monitoring and reporting
You should set up tools to monitor the health and performance of the embedded finance integrations. This includes logging errors, tracking transactions, and even generating financial reports for auditing or business analysis purposes.
In case you are not particularly enthusiastic about handling all the detailed technicalities yourself, consider partnering with a trusted software development agency.
4 Examples of Embedded Finance Products
Understanding the essence of embedded finance is important. Yet, having an appropriate insight into its real-life implementation is even more significant. Let’s review four major examples of embedded finance services and products, so it’s clear how you, as a C-level executive, can apply the technology:
#1 Embedded Banking
Embedded banking implies providing a non-financial institution with a branded checking bank account, enabling it to hold funds, make payments, track expenses, and withdraw earnings seamlessly. The concept which powers up the embedded capabilities here is called open banking. The best thing about it for businesses is that all the functionalities are accessible via their primary platforms and their work interfaces.
Use case: Shopify’s “Shopify Balance” for merchants. Shopify, a predominant e-commerce platform, offers a dedicated business account directly within the Shopify ecosystem, streamlining cash flow tracking and expense management. This embedded financial solution eliminates the barriers of traditional banking.
You can familiarize yourself with the general overview of how embedded banking works from the below infographics:

#2 Embedded Payments
Embedded payments are transaction functionalities natively integrated into applications, eliminating the need for third-party payment gateways or external processes. This means that end users of business platforms can make payments, preload funds, and manage their finances without leaving the primary platform or app they’re using.
Use case: Stripe company provides financial infrastructure for businesses worldwide and empowers them to process transactions within non-financial platforms. While embedded banking as one of the embedded finance examples, is about accessing core banking services, like loans or savings, embedded payments are just about enabling one to send and receive money or pay for something.
One of Stripe’s prominent clients is the global e-commerce company Shopify.
#3 Embedded Lending
Embedded lending is the integration of lending services within platforms not traditionally associated with loans or credit. Users can send a request for financial credit seamlessly as they shop, engage with services, or manage their activities on these platforms.
Use case: Klarna’s “buy now, pay later” embedded lending proposition. When integrated into online storefronts, Klarna presents shoppers with instant, flexible payment options at checkout. Customers can opt to pay for their items immediately, defer the payment for a short period, or break down their payments into smaller installments over time.
#4 Embedded Insurance
Embedded insurance is the integration of insurance services within platforms that are associated with activities or purchases that carry risks. In this case, embedded insurance can offer tailored insurance policies based on the specific details of the product or service, by a customer’s request.
Use case: Tesla’s car insurance for vehicle owners. Tesla’s embedded insurance product leverages the vast amount of data cars generate and provides competitive rates, especially for drivers who utilize Tesla’s autopilot and safety features. Tesla’s knowledge of its vehicles, combined with real-time data, can result in better risk assessment and, subsequently, more accurate insurance pricing.
For additional insight into the role of merchants in fintech and how they revolutionize traditional services, read another our blog post.
The Benefits of Adopting Embedded Finance
Naturally, the first thing to look out for is what advantages a technology can bring to your business. Here’s the list of major benefits the adoption of embedded financing has to offer:
- Enhanced customer experience: The best thing about embedded finance is that it streamlines financial processes, offering intuitive, one-stop solutions that increase user satisfaction and retention.
- New revenue streams: The technology diversifies business models. It enables the monetization of financial services, driving additional income for financial and non-financial companies.
- Increased engagement: Incorporating the vast embedded finance capabilities keeps users within the platform longer, increasing customer retention and boosting interaction and transaction frequency.
- Operational efficiency: Integrating embedded finance solutions reduces the need for traditional intermediaries, which minimizes added costs and expedites transactions.
- Data insights: Embedded analytics, as one of the offered embedded finance capabilities, helps to gather user spending and behavior data. It drives business strategies and fosters personalized offerings.
Even though embedded finance is regarded as a nice-to-have feature by many, we can assume that it will become a must-have functionality for any non-fintech platform shortly.
The Limitations and Challenges of Adopting Embedded Finance
As with any technology, there are some pitfalls you should be aware of when considering the adoption of embedded fintech capabilities:
- Security concerns: Handling financial transactions on your side implies that you will need to reflect upon security measures to prevent fraud and breaches.
- Integration complexity: Embedding finance might demand tech restructuring, which can be both time and resource-consuming in some cases, depending on the complexity of the intended functionality.
- Steep learning curve: Non-finance companies may face challenges in understanding and navigating the financial landscape effectively. It may include challenges with the lack of financial literacy, building customer trust, integrating new operational processes, and more.
- Compliance & Legal Challenges: Adopting embedded finance may bring about additional costs related to ensuring data privacy, adhering to stringent financial regulations, and obtaining the necessary licenses. Achieving compliance can be complex, and it often requires expert knowledge, potentially leading to increased operational expenses.
However, you shouldn’t be frustrated about embedded finance opportunities since businesses can only evolve when facing and overcoming challenges. Besides, providers of fintech software development services can always give you a helping hand at your request.
You may discover more about the integration of Tap to Pay, i.e., technology for easy payment processing into non-banking digital products from another or blog post.
5 Industries That Benefit from Embedded Finance the Most
While some business domains may not be impacted by embedded finance, others can reap the most advantage of adopting this technology. Examples include the following industries:
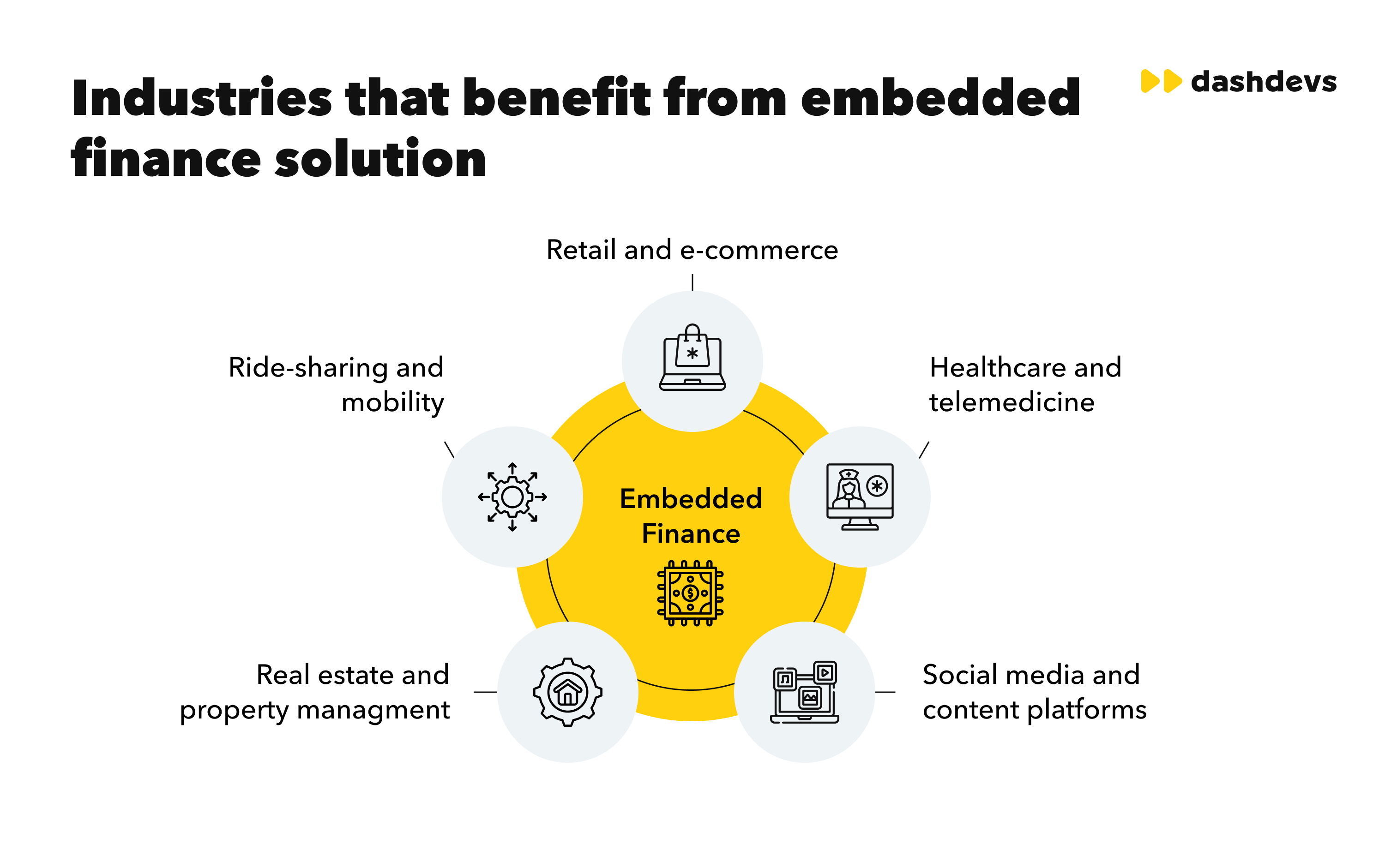
Retail and E-commerce
In the vast landscape of retail and e-commerce, having a smooth flow of financial transactions is absolutely critical for business growth. Embedded finance facilitates this by providing:
- Integrated payments: Allowing for quicker and more flexible payment methods directly on the platform.
- Point-of-Sale lending: Offering instant loans at checkout can enhance customers’ purchasing power.
- Tailored marketing: Leveraging financial data for personalized marketing strategies.
As a result, e-commerce platforms can provide a seamless shopping experience, leading to higher customer satisfaction and increased sales.
Ride-Sharing and Mobility
The mobility sector thrives on convenience and instant solutions. Embedded finance adds to this by:
- Immediate earnings access: Drivers can instantly withdraw their earnings, boosting their liquidity.
- Integrated payments: Riders have various embedded payment options, enhancing their ride experience.
- Customer loyalty programs: Directly integrating rewards to promote frequent usage.
These integrations ensure both drivers and riders enjoy smoother, more efficient transactions and financial benefits.
Real Estate and Property Management
For even a non-financial industry as vast as real estate, making it easy to handle financial aspects can matter a lot. In this domain, embedded finance drives:
- Easy rent transfers: Tenants can pay rent or charges through integrated platforms, ensuring timely payments.
- Property investment: Potential buyers can access instant loans or mortgage options right from property listing sites.
- Operational efficiency: Embedded technologies can automate invoicing and reconciliation tasks.
By integrating these solutions, property management becomes more efficient and user-friendly for both landlords and tenants.
Healthcare and Telemedicine
The healthcare industry is increasingly moving towards digital platforms. Embedded finance aid providers and patents by offering:
- Seamless payments: Patients can make direct payments after a teleconsultation, simplifying the billing process.
- Flexible financing: Providing patients with payment plans or instant loans for treatments.
- Insurance integration: Direct processing of insurance claims and approved payments.
Through these integrations, patients experience a hassle-free healthcare journey, and healthcare providers see improved revenue cycle management.
Social Media and Content Platforms
As the digital content world expands, so does the need for integrated financial solutions. Here is the embedded finance offering for social media:
- Direct monetization: Content creators can receive payments or tips directly on the platform.
- Subscription management: Users can easily manage and renew subscriptions or access premium content.
- Ad revenue: Streamlined processes for advertisers to fund campaigns or pay for ad slots.
By weaving financial processes directly into the platform, content creators, advertisers, and users all experience enhanced financial convenience and growth opportunities.
Since embedded finance is spreading across various domains, it’s likely that we’ll see its inclusion in business environments in many other industries.
Embedded Finance’s Impact on FinTech
At the end of the day, it’s vital not to have either an extremely negative or overly positive attitude towards embedded finance for fintech businesses. Here are the four main challenges and opportunities to keep in mind when considering to develop your fintech software:
- Modified relationships with consumers: Adoption of embedded finance capabilities deepens trust, fosters convenience, and personalizes the experience of end users of financial services.
- New revenue streams: The technology can help diversify income sources by integrating profitable financial services into non-financial platforms. Revenue options that can be explored here include transaction-based and subscription-based models, as well as forming partnerships with financial service providers.
- More partnerships: Embedded finance, by its nature, focuses on fostering collaborations between fintech, non-fintech, tech firms, and traditional banks. It should result in the emergence of comprehensive offerings.
- Greater competition: As with most game-changing technologies, embedded finance intensifies rivalry, pushing firms to innovate, adapt, and offer unique value propositions.
Anyway, embedded finance has already played a role in reshaping the fintech domain, and its influence definitely won’t wear out in the near future.
Final Take
The embedded finance revolution is another opportunity for both traditional providers and non-fintech businesses to enhance user experience and acquire new revenue streams. Since more and more businesses offer embedded finance products, including this option in your platform becomes crucial to stay competitive.
Partnering with a trusted developer and a provider of fintech consulting services is already half the battle. With vast experience and industry-best expertise, DashDevs company can help you get the most out of the embedded finance and digital transformation capabilities it brings.
Contact us today to book your free strategy session. Let’s discuss the embedded finance or other IT opportunities for your business.








