ISO 8583: The Essential Standard for Credit Card Transactions
As a fintech leader, you know the stakes: every failed payment, every delayed transaction, and every missed integration with a bank or card network translates to lost revenue and frustrated customers. The solution? Implementing ISO 8583—the standard that powers global card payment systems.
ISO represents an opportunity to create payment systems that operate seamlessly across borders, scale with ease, and foster trust with customers and partners alike. By embracing ISO 8583, you set your business up for innovation, growth, and long-term resilience in a competitive market.
This article will guide you through the essentials of ISO 8583, helping you understand its value and why it’s critical for building a payment product that stands out in today’s financial ecosystem.
Introduction to ISO 8583
ISO 8583 is an international standard for the interchange of electronic transactions initiated by cardholders.
It defines a message format and data elements that allow point-of-sale (POS) terminals, ATMs, and payment processors to communicate effectively.
At its core, ISO8583 serves two primary purposes:

ISO’s significance lies in the efficiency it brings to global financial transactions, ensuring that millions of daily payments are processed accurately and securely.
Over the years, ISO 8583 has undergone several updates to accommodate the rapidly evolving financial landscape and technological advancements. These versions include the following:
ISO 8583:1987
- Introduced a foundational messaging structure for payment transactions
- Standardized key elements such as transaction types, response codes, and error handling
- Faced limitations in adaptability to emerging technologies and growing transaction complexities
ISO 8583:1993
- Enhanced the structure by introducing additional message types and data elements
- Improved support for multi-currency transactions and international operations
- Addressed inconsistencies found in the 1987 version
ISO 8583:2003
- Reflected the rise of digital payments and modernized banking systems
- Introduced fields for new payment methods, such as e-commerce and contactless transactions
- Improved extensibility to align with future payment innovations
You can also read a detailed article on ISO 20022 to compare it with the newer one.
ISO 8583 started as a basic communication protocol for credit card processing standards but has evolved into a dynamic and extensible standard capable of supporting the complex and diverse requirements of today’s digital transformation services.
So, let’s proceed with how this method works in detail.
How ISO 8583 Works on the Example of An Online Payment
Understanding how a credit card’s standard dimensions work might seem complicated, but it’s actually a straightforward process when you break it down. The diagram below shows the journey your payment takes when you use your card, whether you’re swiping it at a store, inserting it at an ATM, or entering the details online. Let’s walk through it together, step by step.
#1 Cardholder starts the payment
It all begins when a cardholder uses a card to make a payment. This could be at a store’s terminal, an ATM PAI ISO, or even an online checkout page.
#2 Merchant terminal formats the transaction
The terminal collects your payment details (like card number and amount) and organizes them into an ISO merchant processing message, which is a special format that ensures all systems understand it.
#3 Message goes to the acquirer bank
The terminal sends the formatted message to the merchant’s bank, often called the acquirer. This bank handles payments for the merchant and forwards the request.
#4 Card network routes the message
The acquirer sends the message to the card network, e.g.Visa or Mastercard. The card network’s job is to figure out which bank issued your card and send the message there.
#5 Issuer bank checks the details
Your bank, the issuer, receives the message and performs several checks:
- Verification of the transaction isn’t fraudulent
- Fraud checks if you have enough money or credit available
- Payment follows the bank’s rules
If everything checks out, the bank approves the transaction. If there’s a problem, it denies it.
#6 Response travels back: The issuer bank sends a response (approval or denial) back through the ISO credit card processing network to the acquirer and finally to the merchant’s terminal.
#7 The result is displayed: The terminal shows the transaction result—approved or declined—and complete the purchase if it is approved.
Although this process only takes a few seconds, it involves numerous behind-the-scenes processes to ensure a smooth and secure payment. The ISO8583 standard makes sure every step is clear and consistent, no matter where you use your card.

This diagram helps you visualize the journey of your payment, showing how the cardholder, merchant, acquirer bank, card network, and issuer bank all work together to complete the transaction.
So, ISO merchant processing ensures that every party in the chain communicates efficiently and securely, enabling millions of transactions to happen every day with incredible speed and reliability.
Structure of ISO 8583 Messages
The strength of ISO payment processor lies in its structured approach to organizing transaction data. Every ISO message follows a specific format, ensuring consistency and clarity during communication between parties in a transaction.
An ISO message is made up of the following main parts:
Message Type Indicator (MTI)
The MTI is a 4-digit numeric code that specifies the type of message being sent. It indicates the purpose of the message (e.g., request, response, or notification) and the context in which it is being used.
Format of MTI: xxxx
- First digit: Version of the ISO 8583 standard (e.g.,
1for 1987,2for 1993,3for 2003). - Second digit: Class of the message (e.g.,
1for authorization,2for financial transactions). - Third digit: Function (e.g.,
0for request,1for response). - Fourth digit: Origin (e.g.,
0for original,1for repeat).
Example of MTI:
1200: Authorization request using the 1987 standard.2210: Financial transaction response using the 1993 standard.
Bitmap
The bitmap is a unique feature of ISO 8583. It is a string of bits (0s and 1s) that indicates which data elements are present in the message.
Structure:
- A bitmap can be 64 bits (primary) or 128 bits (extended).
- Each bit corresponds to a specific data element (e.g., bit 2 represents the primary account number).
Example:
If the bitmap is 10000010 00000001, it means that data elements 1, 2, and 64 are present in the message.
Data Elements (DEs)
Data elements are the key pieces of information that make transactions possible in ISO 8583.
ISO 8583 supports up to 128 data elements, and while not all are used in every transaction, certain DEs play a critical role in common payment processes.
Key data elements include:
- DE 2: Primary Account Number (PAN) – The card number.
- DE 3: Processing Code – The type of transaction (e.g., purchase, refund, or reversal).
- DE 4: Transaction Amount – The value of the transaction.
- DE 7: Transmission Date and Time – The timestamp for the transaction.
- DE 11: Systems Trace Audit Number – A unique ID for tracking the transaction.
- DE 37: Retrieval Reference Number – Used for reconciliation between systems.
- DE 39: Response Code – Communicates the transaction status (e.g., approval or error).
- DE 41: Card Acceptor Terminal ID – Identifies the merchant’s terminal.
Thus, here is how these data elements are used and where:
1. Authorization process
When a customer initiates a payment, the system validates their credit card processing ISO details and account status.
- DE 2 (PAN): Identifies the cardholder.
- DE 4 (Transaction Amount): Specifies the purchase amount.
- DE 39 (Response Code): Confirms whether the transaction is approved.

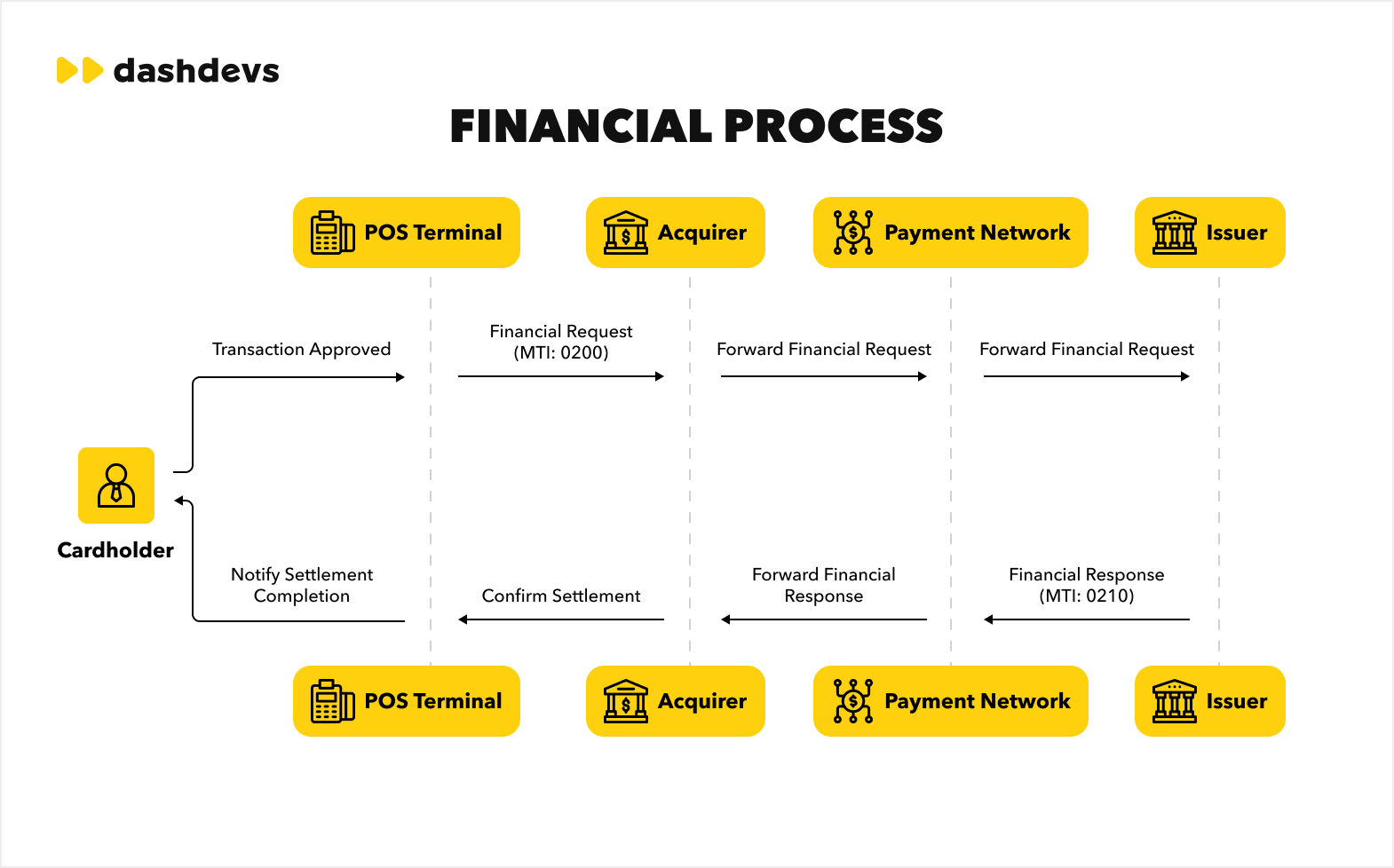
2.Financial process
After a successful transaction, the settlement process ensures funds move from the cardholder’s bank to the merchant.
- DE 37 (Retrieval Reference Number): Tracks the transaction.
- DE 4 (Transaction Amount): Confirms the exact amount transferred.
3. Reversal process Reversals occur when an error needs to be corrected, or a transaction is canceled.
- DE 11 (Systems Trace Audit Number): Identifies the original transaction to reverse.
- DE 39 (Response Code): Indicates whether the reversal was successful.

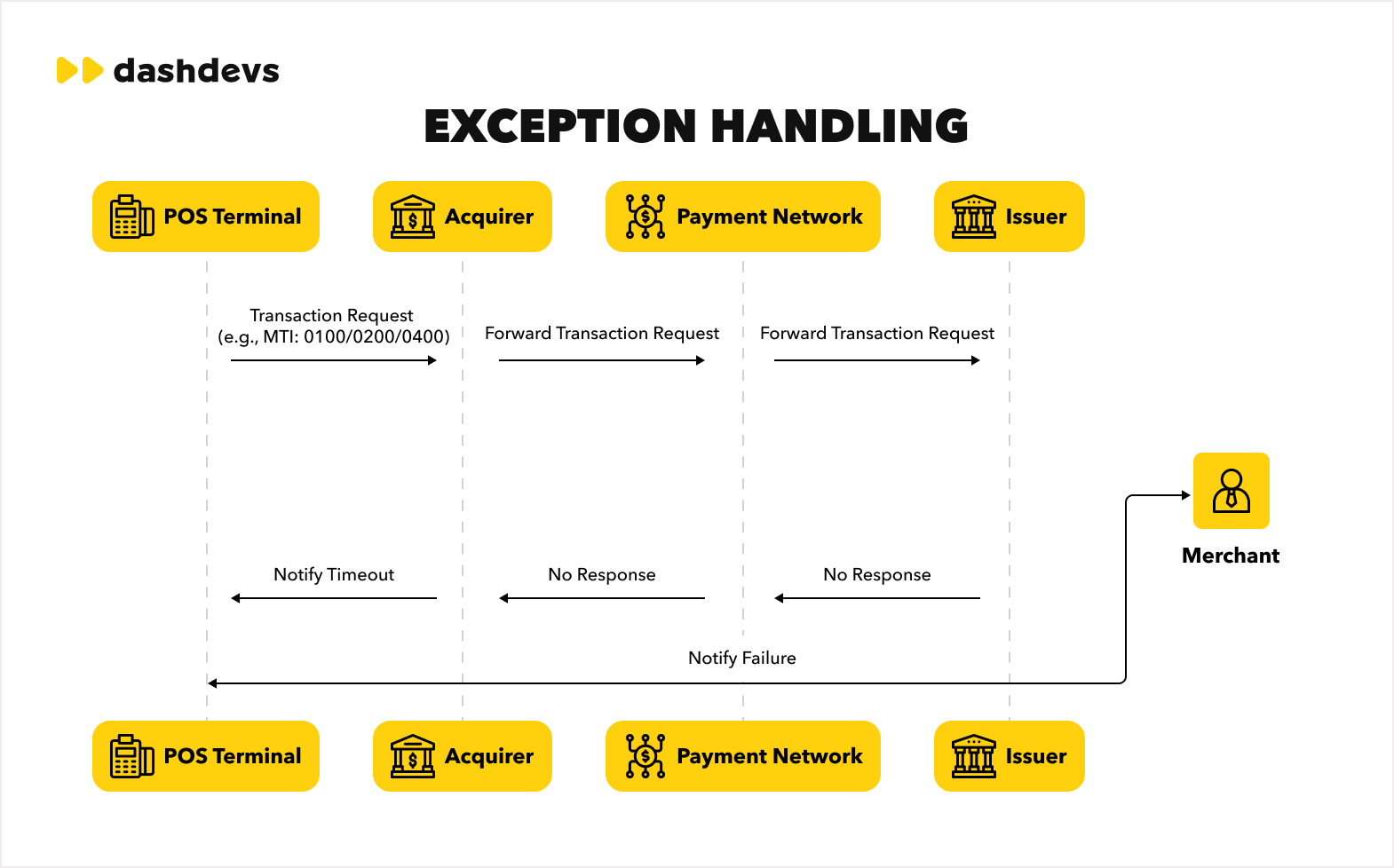
4. Exception handling Timeouts or network errors can interrupt transactions. ISO 8583 handles these situations by communicating error codes.
- DE 39 (Response Code): Provides error details to diagnose and resolve the issue.
5. Refund Process Refunds allow merchants to return funds to the customer’s account.
- DE 3 (Processing Code): Identifies the transaction as a refund.
- DE 4 (Transaction Amount): Specifies the amount to be refunded.

Why Businesses Should Comply with ISO 8583
ISO 8583 compliance is critical for businesses involved in payment processing, whether they are merchants, banks, fintech companies, or card networks. By adhering to this standard, businesses ensure smooth, secure, and efficient financial transactions.
Below are the key reasons why ISO 8583 compliance is essential and how it delivers tangible value.
Seamless Payment Processing
ISO 8583 acts as a universal language for financial transactions, enabling interoperability between different systems. Compliance ensures:
- Global compatibility: Businesses can communicate with any card network, acquirer, or issuer without worrying about system mismatches.
- Fewer errors: Standardized messaging reduces the risk of miscommunication or transaction failures.
- Scalability: As businesses grow and expand internationally, ISO 8583 ensures that their payment systems work globally.
Example: A small e-commerce store complying with ISO 8583 can accept card payments from customers in any country, boosting sales and reach.
Enhancing Security
Payment data security is a top priority, and ISO 8583 compliance integrates robust security mechanisms to protect sensitive information like card numbers and transaction details.
- Data encryption: Ensures cardholder information is secure during transmission.
- Fraud prevention: Reduces the risk of fraudulent transactions by providing clear and secure communication protocols.
- Customer trust: Businesses that comply with ISO 8583 are seen as more secure and reliable by customers.
Example: A retail chain with ISO 8583-compliant systems faces fewer chargebacks and security breaches, saving money and preserving its reputation.
Innovation and Modern Payment Methods
ISO 8583 is adaptable, allowing businesses to seamlessly integrate modern payment methods like contactless, mobile payments, and Buy Now, Pay Later (BNPL).
- Future-proof systems: Compliance ensures that businesses are ready to support emerging payment trends.
- Integration flexibility: New fintech solutions can integrate with legacy systems using ISO 8583.
Example: A fintech offering BNPL services can use ISO cards to connect with card networks and banks, enabling a seamless checkout experience for users.
Meeting Regulatory and Partnership Requirements
Many payment networks, banks, and regulators require ISO 8583 compliance as a prerequisite for partnerships. Businesses that comply can:
- Unlock partnerships: Work with major players like Visa, Mastercard, and global banks.
- Avoid penalties: Meet regulatory standards to avoid fines and operational disruptions.
Example: A startup payment gateway must be ISO 8583-compliant to partner with leading card networks and expand its merchant base.
Increasing Operational Efficiency
ISO 8583 reduces inefficiencies in payment processing, saving time and costs.
- Faster transaction times: Standardized messaging ensures quick processing, even during high volumes.
- Fewer disputes: Accurate and secure communication reduces errors and transaction reversals.
Example: A payment processor complying with ISO 8583 can handle a large volume of transactions during peak shopping seasons without delays or errors.
Delivering Business Value
ISO 8583 compliance offers several benefits that directly impact a business’s bottom line:
- Increased revenue: By enabling global payments, businesses can serve a wider audience.
- Customer loyalty: Faster and more secure payments lead to a better customer experience.
- Cost savings: Reduced errors, fraud, and chargebacks save businesses money.
- Competitive advantage: Businesses with ISO 8583 compliance are more attractive to partners and customers.
Example: An international hotel chain with ISO 8583-compliant systems can accept payments from customers worldwide, ensuring a smooth booking experience while reducing operational risks.
ISO 8583 ensures global compatibility, enhances security, supports innovation, and reduces costs, making it indispensable for businesses in the payments ecosystem. Whether you’re a merchant, a bank, or a fintech startup, aligning with ISO 8583 helps you grow, scale, and remain competitive.
To Conclude
By now, you should have a clear understanding of why ISO 8583 compliance is essential for businesses handling card transactions. This standard serves as the foundation for global payment processing, enabling seamless communication, secure transactions, and efficient operations. Whether you’re developing a new payment system or growing your fintech product, ISO 8583 guarantees scalability, reliability, and compatibility with the global financial ecosystem.
Our team of experts offers extensive consultation on ISO 8583 to make your transition seamless and efficient. Whether it’s ensuring compliance, building robust payment infrastructures, or scaling your fintech product, our team is equipped to guide you every step of the way. Reach out to DashDevs today to discuss how we can power your payment solution for global success.

