What is a Transaction Processing System (TPS): Types and Usages
In 2026, transaction processing systems sit at the core of modern financial infrastructure. What was once back-office software has become frontline architecture for payments, banking, trading, e-commerce, and embedded finance. As transaction volumes rise and settlement expectations move toward real-time, a transaction processing system increasingly determines whether a product can scale, remain compliant, and operate reliably under pressure.
Global digital payment transaction value is projected to reach USD 20.37 trillion in 2026, growing at a 15.90% CAGR toward USD 38.07 trillion by 2030. This growth places the transaction processing system at the center of operational resilience, regulatory compliance, and customer-facing performance.
This article explains what a transaction processing system is, how a TPS system works, its components, characteristics, and types, and how transaction processing systems are used in real-world financial products. Market dynamics, regulatory pressures, and architectural trends shaping TPS design are also examined, with practitioner insight drawn directly from production fintech environments.
Summary
- What is a Transaction Processing System (TPS)?
- Examples of TPS
- Functions of TPS
- Characteristics of TPS
- Components of TPS
- Types of TPS
- Applications of TPS in payments and remittances
- Perks of TPS
What is a Transaction Processing System?
A transaction processing system (TPS) is an information system designed to collect, validate, process, store, and retrieve transactional data generated by day-to-day business operations.
The definition TPS used in information systems focuses on reliability, consistency, speed, and auditability. A transaction processing system ensures that each transaction is processed exactly once, recorded accurately, and reflected consistently across all dependent systems. In practice, this includes payments, balance updates, order execution, inventory changes, and settlement records.
TPS stands for Transaction Processing System. The term transaction information system is often used interchangeably, although transaction information system typically emphasizes data capture and reporting, while a TPS system includes enforcement of business rules, integrity guarantees, and recovery mechanisms.
It is important to separate the concept of a transaction processing system from payment rails themselves. A TPS system does not move funds across card networks, ACH, wires, or blockchains. Instead, it orchestrates, validates, and records the transactions that flow through those rails.
Transaction Processing System Market Overview
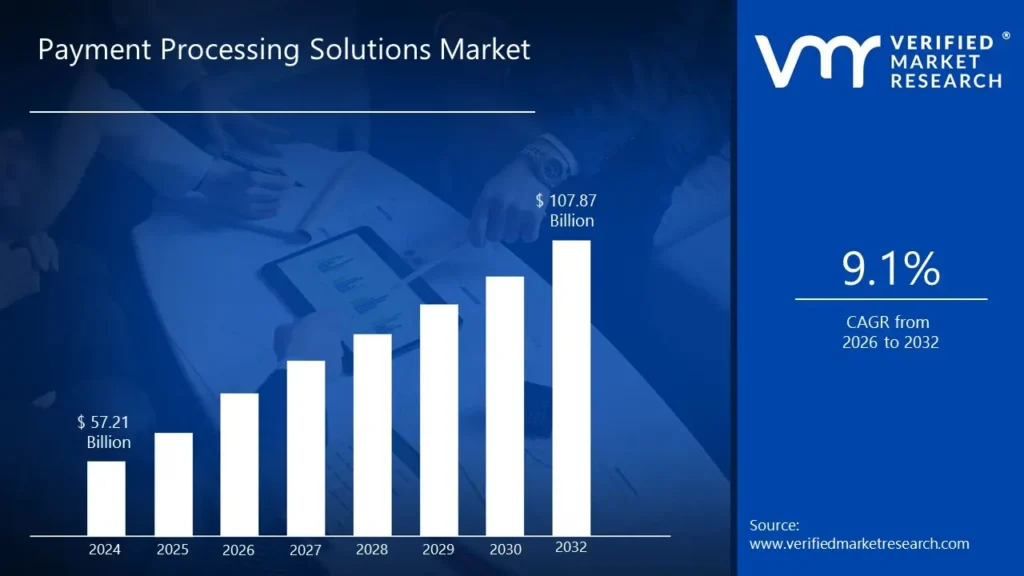
The transaction processing system market is expanding alongside global payment modernization. The broader payment processing market reached USD 176.07 billion in 2026, up from USD 152.01 billion in 2025, driven by rising digital transaction volumes .
Fintech-as-a-Service platforms represent a major delivery model for modern TPS systems. The FaaS market is projected to grow from USD 470.94 billion in 2025 to USD 906.14 billion by 2030, reflecting a shift toward modular, API-first transaction processing.
Real-time payments are the most transformative TPS segment. Global instant payment volume exceeded USD 60 trillion in 2025, with transaction counts projected to double from 266 billion in 2023 to 575 billion by 2027.
Regionally, North America accounts for roughly 34% of the payment processing market, Europe 28%, and Asia-Pacific 26%, with Asia-Pacific showing the fastest growth due to mobile wallets, QR-based payments, and government-led cashless initiatives.
Examples of Transaction Processing Systems
Transaction processing system examples appear across industries where accuracy, speed, and consistency are required.
Banking ATMs rely on TPS infrastructure to authenticate customers, retrieve account data, update balances, and dispense cash in real time.
Stock exchanges and trading platforms use high-throughput transaction processing systems to match orders, execute trades, update positions, and settle transactions with strict sequencing and durability requirements.
Airline reservation systems depend on TPS platforms to check seat availability, process payments, issue tickets, and generate confirmations without double booking.
E-commerce platforms use a TPS system to validate payments, update inventory, generate receipts, and record transactions for reconciliation and reporting. Dive deeper into Merchant transaction processing here.
Healthcare and billing systems apply transaction processing systems to manage patient billing, insurance claims, and payment records where accuracy and auditability are mandatory.
Our first-hand experience
In crypto and multi-asset trading environments, transaction processing systems operate under extreme consistency and latency constraints. DashDevs delivered a full-stack digital assets trading platform supporting market execution, liquidity management, multi-currency wallets, and compliant crypto–fiat flows. Each trade, settlement event, and balance update is processed as a discrete, time-sensitive transaction, highlighting the TPS role in ensuring integrity across multiple financial rails.
DashDevs perspective:
In fintech product builds, TPS constraints usually surface first at integration points. When connecting card processors, banking cores, and ledgers, transaction finality, rollback behavior, and reconciliation logic must align across multiple vendors. These integration boundaries are where theoretical TPS models meet operational reality.
Functions of Transaction Processing Systems
Runtime Functions
A transaction processing system performs several core runtime functions:
- Transaction validation and execution
- Concurrency control to prevent conflicting updates
- Data integrity enforcement across services and ledgers
- High availability under peak load
- Security controls for sensitive transaction data
- Real-time and post-processing reporting
DashDevs perspective:
In production systems, these functions are rarely delivered by a single monolithic TPS. Runtime processing, durability, and observability are often split across domain services, event streams, and ledger components to support scale and regulatory traceability.
System Administration Functions
Administrative functions include configuration management, monitoring, alerting, and operational controls. These capabilities allow organizations to adapt TPS behavior to regulatory changes, new payment rails, or regional deployment requirements.
Application Development Functions
Modern TPS platforms expose APIs and SDKs that allow product teams to build applications on top of transaction infrastructure. These interfaces support customization, orchestration, and controlled extension without compromising core processing guarantees.
Characteristics of Transaction Processing Systems
An effective transaction processing system exhibits the following characteristics:
- Rapid response times, often sub-second
- Standardized and repeatable processing logic
- Reliability supported by redundancy and recovery mechanisms
- Controlled workflows aligned with business and regulatory rules
- Real-time processing for customer-facing interactions
- Strong concurrency control
- ACID compliance for financial correctness
- High throughput, often thousands of transactions per second
DashDevs perspective:
Many fintech scalability issues originate not from business logic but from overlooked TPS characteristics such as idempotency, retry handling, and recovery semantics. These properties only become visible once transaction volume and integration complexity increase.
Components of a Transaction Processing System
Our first-hand experience:
In BNPL and repayment-heavy environments, the transaction processing unit and ledger components become central to system correctness. DashDevs built a payment orchestration platform that centralizes repayment collection across cards, wallets, tokenized payments, and bank-to-bank methods. A unified ledger tracks transaction flows across rails and currencies, enabling reconciliation and reporting accuracy while sustaining peak loads exceeding 10,000 payment requests per second.
A TPS system typically consists of four core components:
- Input: Transaction requests such as payment instructions, trade orders, or account updates
- Transaction processing unit: The logic layer that validates, sequences, and executes transactions
- Database or ledger: Durable storage for transactional records
- Output: Confirmations, receipts, reports, and downstream events
DashDevs perspective:
In modern architectures, these components are often distributed. Input handling may live in APIs or gateways, processing logic in domain services, and durability enforced through event stores or ledger services rather than a single centralized database.
Types of Transaction Processing Systems
Real-Time Transaction Processing
Real-time TPS platforms process transactions immediately as they occur. They are essential for online banking, instant payments, trading platforms, and reservation systems where immediate confirmation is required.
Batch Transaction Processing
Batch transaction processing groups transactions and processes them at scheduled intervals. Common batch use cases include payroll, invoicing, settlement, and reconciliation.
Most production systems operate in hybrid mode, combining real-time authorization with batch settlement and reporting.
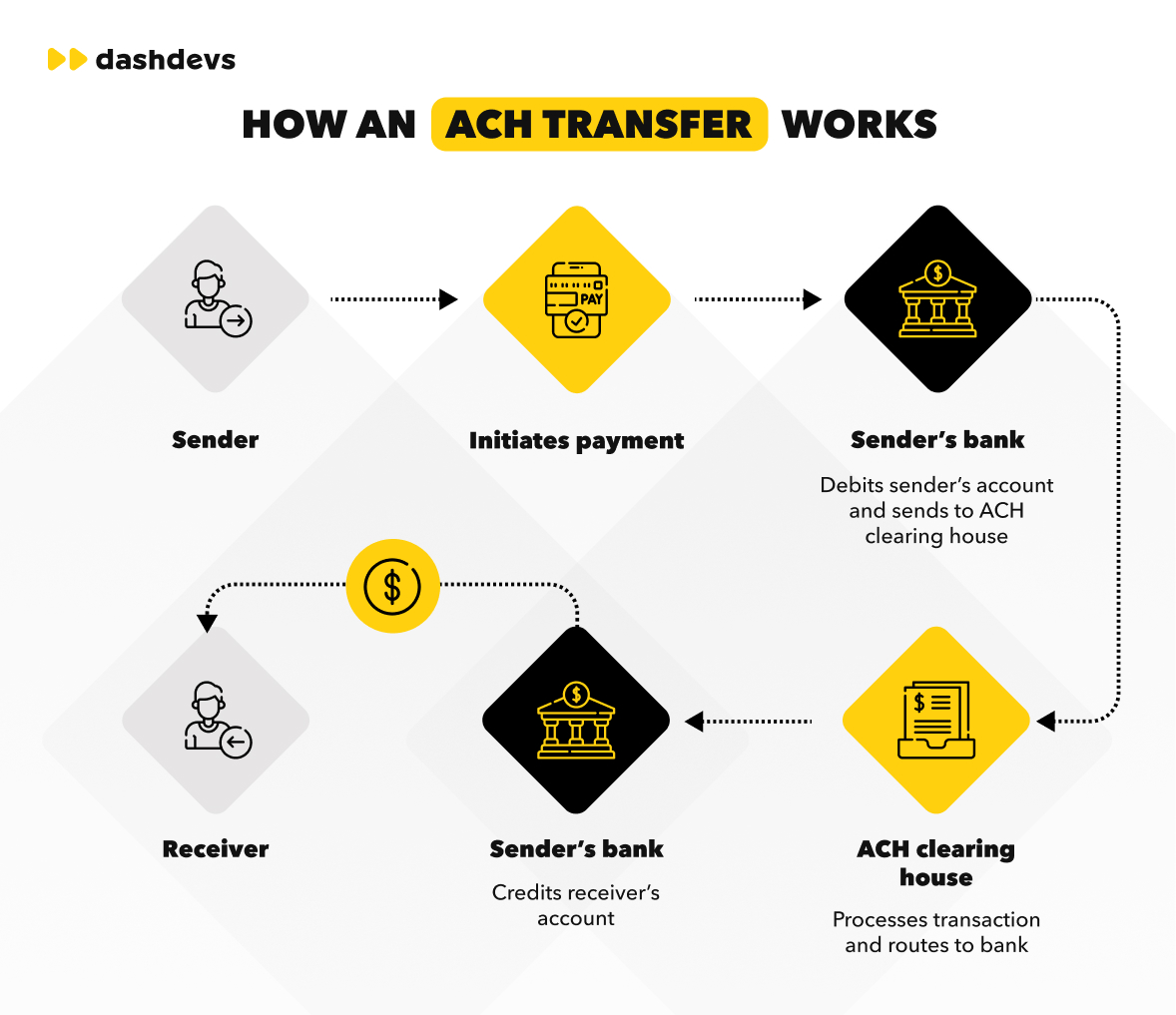
When comparing transaction types such as ACH and wire transfers, a TPS system ensures consistent validation, traceability, and reconciliation regardless of settlement speed.
DashDevs perspective:
Client systems frequently require both real-time customer feedback and deferred settlement flows. This hybrid approach reflects regulatory and accounting realities rather than purely technical preference.
Transaction Processing Systems in Payments and Remittances
Cross-border payments and remittances rely heavily on transaction processing systems to manage currency conversion, compliance screening, settlement timing, and reconciliation across jurisdictions. A practical overview of TPS usage in remittance flows is available here.
Our first-hand experience
Challenger banking platforms demonstrate how transaction processing systems underpin regulated payment and remittance flows. DashDevs helped launch a UK digital bank by engineering a proprietary core banking platform with independently scalable transaction-processing components. The system orchestrates transactions across cards, FX, savings, investments, and third-party providers, while maintaining the audit trails and reporting controls required for FCA regulation.
DashDevs perspective:
Payment orchestration platforms must coordinate multiple rails, retry logic, and ledger updates while preserving a single source of truth. This orchestration layer is often the most critical TPS component in payment-heavy products.
Advantages of Using Transaction Processing Systems
Organizations adopt transaction processing systems to achieve:
- Higher operational efficiency
- Reduced manual errors
- Lower processing costs at scale
- Predictable performance under load
- Global payment and currency support
- Durable audit trails for compliance and reporting
Wrapping Up
A transaction processing system is foundational infrastructure for any organization handling financial transactions at scale. As real-time payments, embedded finance, and digital assets mature, TPS platforms are evolving from simple record-keeping systems into orchestration layers connecting multiple payment rails, asset types, and regulatory frameworks.
For teams building or modernizing financial products, investing in a scalable, compliant, and well-architected transaction processing system is no longer optional. It is a prerequisite for long-term resilience and growth.

